The development of technology is a wonderful thing, but some scammers can take advantage of it.
There is lots of fake news and misinformation about the pandemic being reported regularly, but there's something else to look out for - scams.What are the different ways scams can affect us, and how can we be on the look out for them during the pandemic? Here is some advice about emerging coronavirus scams.

How have scams evolved?
Fraud has existed for centuries. As technology has developed, scammers have evolved from doorstep fraudsters to cyber criminals. While phone and in-person fraud still exists, nowadays youāre more likely to see scams online, via texts, emails and āphishingā messages.
Phishing is the attempt to obtain sensitive information or data, such as usernames, passwords and credit card details, by disguising an email or text as being from a trustworthy source. The term 'Phishing' was coined in the '90s and is still the most common way cyber criminals will try to gain information. Modern phishing can be very sophisticated, especially with accessible information via social media, so itās important to be on the lookout.

What do Covid-19 scams look like?
While coronavirus scams can happen on our doorstep - for example, scammers offering to do peopleās shopping and then not returning after taking the money, or asking people to donate to fake charities and causes - youāre more likely to come across them online.
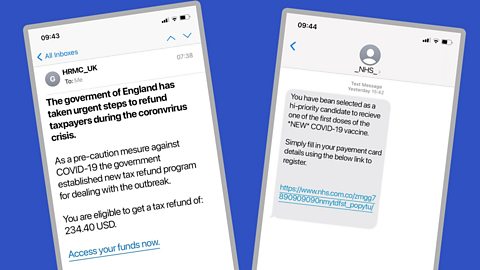
Examples of Covid scams include:
- Emails which trick people into opening harmful links and attachments by offering information about coronavirus
- Emails offering access to "Covid-19 relief funds", which encourage you to share personal information
- Phishing emails that say someone you know has contracted coronavirus - these can lead you to ācopycatā websites (websites which look very similar to official ones) which ask you to share personal details.
- Unexpected texts claiming to be from the government, your GPās surgery, the NHS, or even the World Health Organisation (WHO), which offer information about the virus

How can you protect yourself from these scams?
Criminals can use publicly available information about you to make their phishing messages more convincing. This could be taken from your social media accounts - have a think about what youāre posting and never display important personal details in your bios.
Here are a few more precautions you can take to protect yourself from scams:
- Be wary of information thatās too good to be true - for example, if a message is claiming to have a coronavirus vaccine or is promoting products to protect against or treat the virus. Check the news for official NHS updates or check with your GP
- Never open an attachment from someone you donāt know as these can contain viruses
- If you think a website might be a copycat website, double check the URL
- Never click on a link unless you know itās legit
- Never ever give out your bank account details if youāve clicked on a suspicious link and are prompted to do so.
If you suspect you're receiving fake news about the virus, go to a trusted source such as:

Where next?
Use these simple tips to spot suspicious images.

Coronavirus: How can you stop the spread of misinformation?
A look at how we can all slow the spread of harmful coronavirus advice on social media.

Tips for spotting fake news online
Nihal Arthanayake looks at some simple steps which will help separate fact from fake.

Fact or Fake?
Find out how to spot and stop fake news with “óĻó“«Ć½ Bitesize.
