Electricity, energy and waves
Electric circuits – WJEC
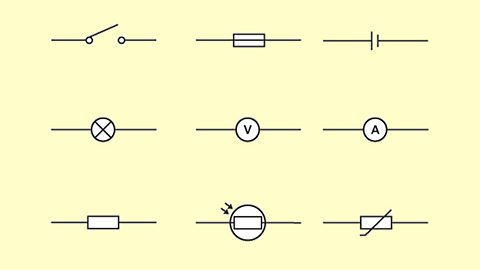
Engineers connect components in electrical circuits in series or parallel to make a range of useful circuits. We can calculate the voltage, current and resistance in these circuits.
Generating electricity – WJEC
Electricity is a convenient source of energy and can be generated in a number of different ways using either fossil fuels or renewable and sustainable technologies.

Making use of energy – WJEC
Heat energy can be transferred from areas of high energy to areas of lower energy by conduction, convection and radiation. Understanding how to control these processes helps reduce energy consumption.

Domestic electricity – WJEC
Domestic electricity explores electrical circuits and the safety devices around the home, like fuses and circuit breakers, the ring main circuit and the functions of the live, neutral and earth wires.

Features of waves – WJEC
Key terms for the features of waves are introduced, and the properties and uses of the EM spectrum, wave speed calculations and satellite communication are also covered.
The total internal reflection of waves – WJEC
This topic explores the conditions necessary for total internal reflection of light. It discusses applications of total internal reflection using optical fibres, like medical uses and communication.
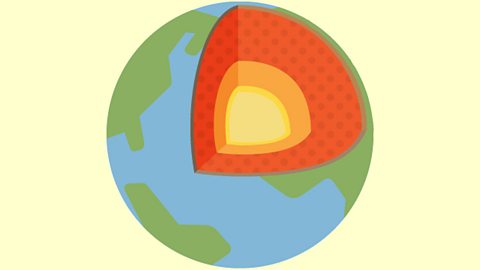
Seismic waves – WJEC
Earthquakes produce shockwaves called seismic waves. These waves can be detected using seismographs. Some seismic waves are surface waves, while others can travel through the Earth.
Kinetic theory – WJEC
Learn about kinetic theory, which includes using the Celsius and Kelvin scales, the relationship between pressure, temperature and volume in gas, and energy changes when changes in state occur.

Electromagnetism – WJEC
If electric current flows in a coil, it experiences a force and moves. Spinning a magnet in a coil of wire generates electricity. Transformers change the size of alternating voltages.

- 6 videos

Forces, space and radioactivity
Distance, speed and acceleration – WJEC
The motion of an object can be predicted by analysing the forces that act on the object. Balanced forces have no effect, while unbalanced forces can lead to change in acceleration.

Newton’s Laws – WJEC
In 1687, Isaac Newton created three laws of motion to describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and how the body moves in response to those forces.

Work and energy – WJEC
Work and energy looks at GPE, KE and elastic energy, and how they are conserved. It also looks at the relationship between force and extension, as well as how car features absorb energy in a crash.

Further motion concepts – WJEC
Moving objects have momentum, and forces cause it to change. The total momentum in an explosion or collision is conserved and stays the same. Equations of motion apply to uniformly accelerated motion.

Stars and planets – WJEC
The Earth forms part of a family of eight planets which orbit around the Sun. This solar system forms part of a huge collection of stars which form the Universe and are also known as galaxies.
The Universe – WJEC
The study of atomic absorption spectra allows us to determine the chemical make-up of stars. It shows that galaxies are moving away from us in an expanding Universe.

Types of radiation – WJEC
Three subatomic particles have different charges and masses. Radioactive particles decay and release alpha, beta and gamma radiation - natural and artificial sources of background radiation.

Half-life – WJEC
Radioactive isotopes are used for blood flow monitoring, cancer treatment, paper mills, carbon dating and smoke alarms. Each isotope used in these applications has a characteristic half-life.

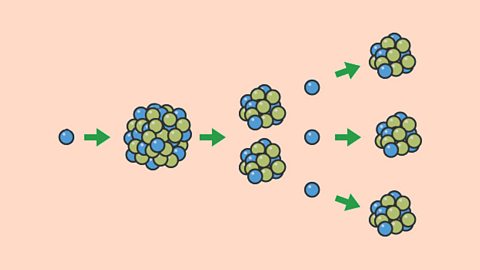
Nuclear decay and nuclear energy – WJEC
Nuclear fission is the splitting of a radioactive nucleus to release energy. High-energy collisions between light nuclei can result in fusion, which releases energy.
- 7 videos

Practical skills
Obtaining, analysing and evaluating results – WJEC
Under the new GCSE specifications in Wales, practical work in Science will be examined. This unit will help students to prepare for the practical examination.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link