Mitosis and the cell cycle
Mitosis
Cells divide when:
- an organism grows
- an organism becomes damaged and needs to produce new cells
It is essential that any new cells produced contain genetic information that is identical to the parent cell. All new cells are created from existing cells when they divide.
The cell cycle
A growing and dividing cell goes through a series of stages called the cell cycleThe events that lead to cell division and DNA replication..
The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then replicationThe doubling of the chromosomes resulting from the copying of DNA to produce chromatids before mitosis of DNADeoxyribonucleic acid. The material inside the nucleus of cells, carrying the genetic information of a living being.. The single strand of DNA that makes up each chromosome produces an exact copy of itself. All of the organelleThe name given to a membrane bound compartment with a specific function in animal, plant and fungal cells. inside the cell are also copied. These processes happen in a stage of the cell cycle called interphaseThe longest phase of the cell cycle, during which a cell copies its DNA..
Once the cell has completed all the necessary processes during interphase, it is ready to enter into the next stage of cell cycle. The cell now undergoes a type of cell division called mitosisA type of cell division which produces daughter cells identical to the parent..
In mitosis, the chromosome copies separate, the nucleus divides and the cell divides. This produces two cells called daughter cellsCells formed from the division of a cell.. Each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell and to one another.
The organism now has more cells and so has grown.
Observing stages of mitosis
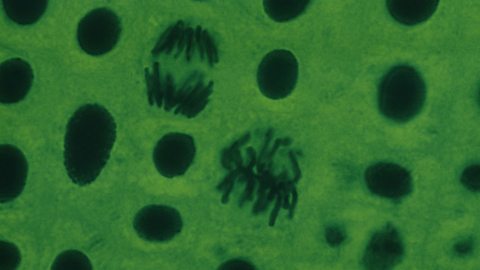
A light microscope can be used to observe cells during the cell cycle. The DNA is stained so it can be seen more clearly. When looking down the microscope, the presence of individual chromosomes shows that the cell is in the mitosis stage of the cell cycle. If chromosomes cannot be seen then the cell is in interphase.
Cancer
cancerA disease caused by normal cells changing so that they grow and divide in an uncontrolled way. The uncontrolled growth causes a lump called a tumour to form. is a non-communicable diseaseA disease that is not transferred between people or other organisms. that is caused by changes in a person's DNA. Normally, cells only divide if they get the correct signal. This could be triggered when the organism needs to grow so more cells are needed, or the organism has an injury so more cells are needed to repair it. If there is a mutationA random and spontaneous change in the structure of a gene, chromosome or number of chromosomes. in the DNA of a person that stops the correct signals being sent to cells, cells may start to divide even though they don't need to. Mitosis is no longer controlled properly. When the cell divides many times by mitosis, a lump of cells can form, which is called a tumourThe lump of cells formed as a result of uncontrolled cell division..
Learn more about mitosis and meiosis with Dr Alex Lathbridge.
Listen to the full series on ґуПуґ«ГЅ Sounds.
In this podcast, learn the key facts about mitosis and meiosis. Listen to the full series on ґуПуґ«ГЅ Sounds.