Development of new materials
Kevlar

Kevlar is a new synthetic polymer which is extremely strong and light.
The polymer chains are rigid and they pack together in sheets making Kevlar very strong. It can be used in aircraft wings, bulletproof vests and other products where strength and weight are important.
Poly(ethenol)
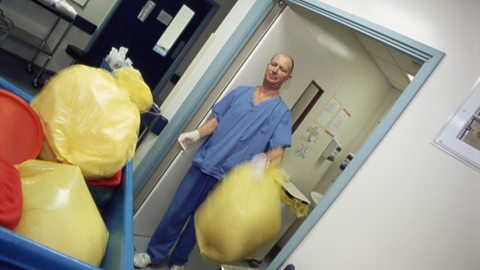
Poly(ethenol) is a polymer that is soluble in water. This breakthrough in synthetic materials is very useful wherever polymers are used as a barrier that is soluble, for example in hospital laundry bags for washing soiled linen.
Biopol
Biopol is a biodegradable polymer that can be broken down by bacteria in soil. By producing food packaging and plastic bottles made of biopol instead of conventional plastics, concerns over waste management can be answered. Since most plastics are non-biodegradable, they must be destroyed by incineration, potentially releasing harmful or toxic gases. Biopol can be disposed of in landfill sites as the material will rot away overtime.
Conductive polymers
Most plastics are natural insulators. The are several advantages of making plastics which are conductors:
- They are easier to manufacture.
- They are lighter and cheaper than metals.
- They prevent the build-up of static electricity which can damage microcircuits.
Some conductive polymers are also biocompatible, making them suitable for use in medical devices.
Nanomaterials
Nanoparticles improve the mechanical properties of a material, such as stiffness or elasticity. When incorporated into polymers, they can be used as lightweight replacements for metals.
Nanomaterials are used in car manufacturing to create cars that are faster, safer and more fuel efficient. They can also be used to produce more efficient insulation and lighting systems.