The skeleton
Our skeletonThe support structure for an organism. In humans, it consists of bones inside the body. is made of more than 200 boneHard, rigid tissue forming the skeleton in humans and other vertebrates.. Calcium and other minerals make the bone strong but slightly flexible. Bone is a living tissueA group of similar cells that carry out the same function, eg muscle tissue. with a blood supply. It is constantly being dissolved and formed, and it can repair itself if a bone is broken.
Function of the skeleton
The skeleton has four main functions:
- to support the body
- to protect some of the vital organs of the body
- to help the body move
- to make blood cells
Support
The skeleton supports the body. For example, without a backbone we would not be able to stay upright.
Protection
Here are some examples of what the skeleton protects:
- the skull protects the brain
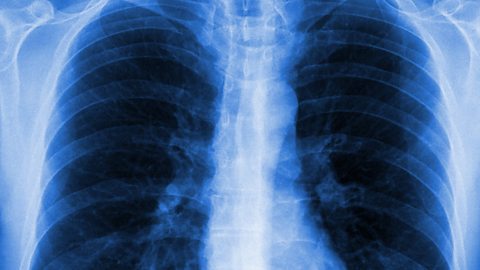
- the ribcage protects the heart and lungs
- the backbone protects the spinal cord
Movement
Some bones in the skeleton are joined rigidly together and cannot move against each other. Bones in the skull are joined like this. Other bones are joined to each other by flexible joints. Muscles are needed to move bones attached by joints.
Making blood cells
There are different kinds of blood cells, including:
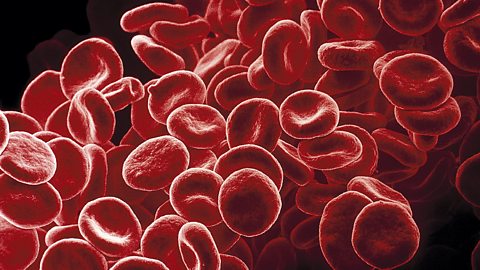
- red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body in the blood
- white blood cells, which are involved in destroying harmful microorganisms in your body
These cells are made in the bone marrow. This is soft tissue inside our larger bones which is protected by the hard part of the bone which surrounds it.
An introduction to the skeletons of humans and other animals