Neurobiology and immunology
Divisions of the nervous system and neural pathways
The nervous system enables humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour. It comprises millions of neurones and uses electrical impulses to communicate very quickly.
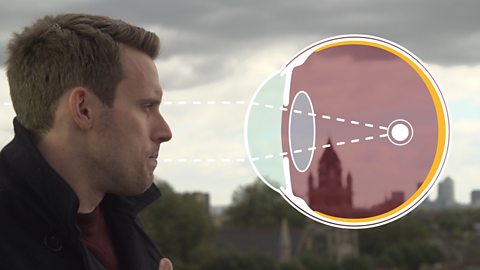
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum in the brain. It is important for helping process language, memory, and thought.

Memory
Memory allows the brain to store and retrieve information when required. Sensory memory takes in information. Short-term memory holds a small amount of information for a short time. Long-term holds an unlimited amount of information for a long time.
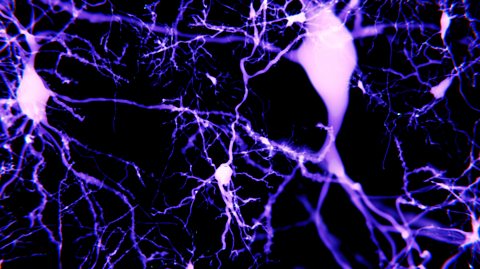
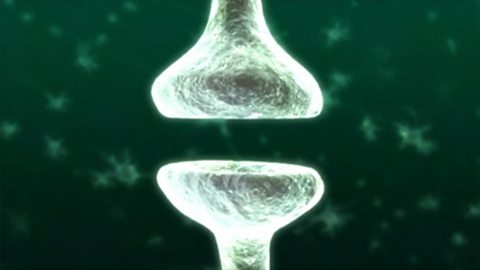
Cells of the nervous system, neurotransmitters at synapses
Your brain contains billions of neurons. They are the cells in the brain that transmit and receive signals to enable processes such as thought. These signals are transmitted across junctions called synapses by neurotransmitters.
Non-specific body defences
The immune system defends humans from pathogens. Physical and chemical barriers prevent infection. White blood cells attack pathogens. Immunisations usually involve injecting inactive pathogens.
Specific cellular defences against pathogens
Lymphocytes are the white blood cells involved in the specific immune response. They produce antibodies that respond to specific antigens on the surface of pathogens. Memory cells remain in the blood stream and lead to a quicker and stronger defence against a secondary infection by the same pathogen.
Immunisation
Vaccination introduces a weak or dead version of a pathogen to the body to bring about immunity. Public vaccination can bring herd immunity for some diseases.
Clinical trials of vaccines and drugs
Clinical trials of vaccines and drugs are carried out to show that they are safe and effective. Tests are randomised, use control groups given placebos, and are carried out double-blind to avoid bias.