Bonding, structure and the properties of matter
The three states of matter - AQA
The three states of matter can be represented by the particle model. This model explains the properties of substances in their different states, as well as changes of state.
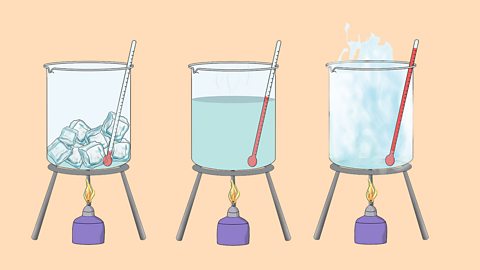
Ionic compounds - AQA
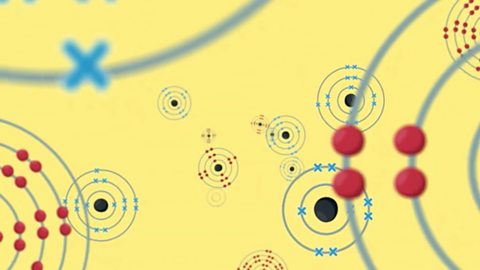
An ionic compound is made up of charged particles, called ions. It has a giant lattice structure with strong electrostatic forces of attraction.

Small molecules - AQA
A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonding forms molecules. Substances with small molecules have low melting and boiling points, and do not conduct electricity.
Giant covalent molecules - AQA
Giant covalent substances have many atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Diamond, graphite and graphene are forms of carbon with different giant covalent structures.

Metals and alloys - AQA
The structure of metals explains their high melting and boiling points and their conductivity. The properties of a metal can be modified by mixing it with another substance to form an alloy.

Nanoscience - AQA
Nanoparticles are 1 nm to 100 nm in size. They have very large surface area to volume ratios. The properties of nanoparticulate substances are different from those of the same substance in bulk.

Sample exam questions - bonding, structure and matter - AQA
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link