Our dynamic universe
Motion - equations and graphs
The motion of objects can be analysed using equations and graphs. These tools allow other aspects of motion such as acceleration and displacement to be determined or modelled.

Forces, energy and power
Forces and the motion of objects can be determined using Newton's Laws of motion.
Collisions, explosions and impulse
Momentum, kinetic energy and impulse can be used to analyse collisions between objects such as vehicles or balls. Forces and the final velocity of objects can be determined.

Gravitation
Projectile motion is analysed in terms of vertical and horizontal components. The gravitational force between objects depends on their mass and the distance between their centres.
Special relativity
The speed of light is constant but length and time can change when objects travel at close to the speed of light. These changes depend on the relative motion of the observer and the object.

The expanding Universe
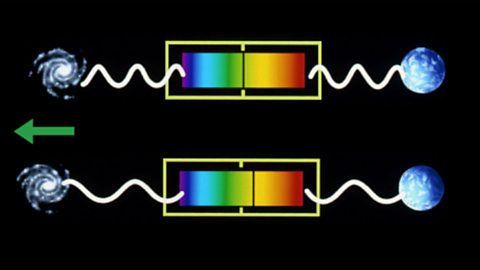
The Doppler effect causes shifts in wavelengths of sound and light. Cosmic microwave background radiation as evidence for the Big Bang and expansion of the Universe.
Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link