By Anisa Subedar


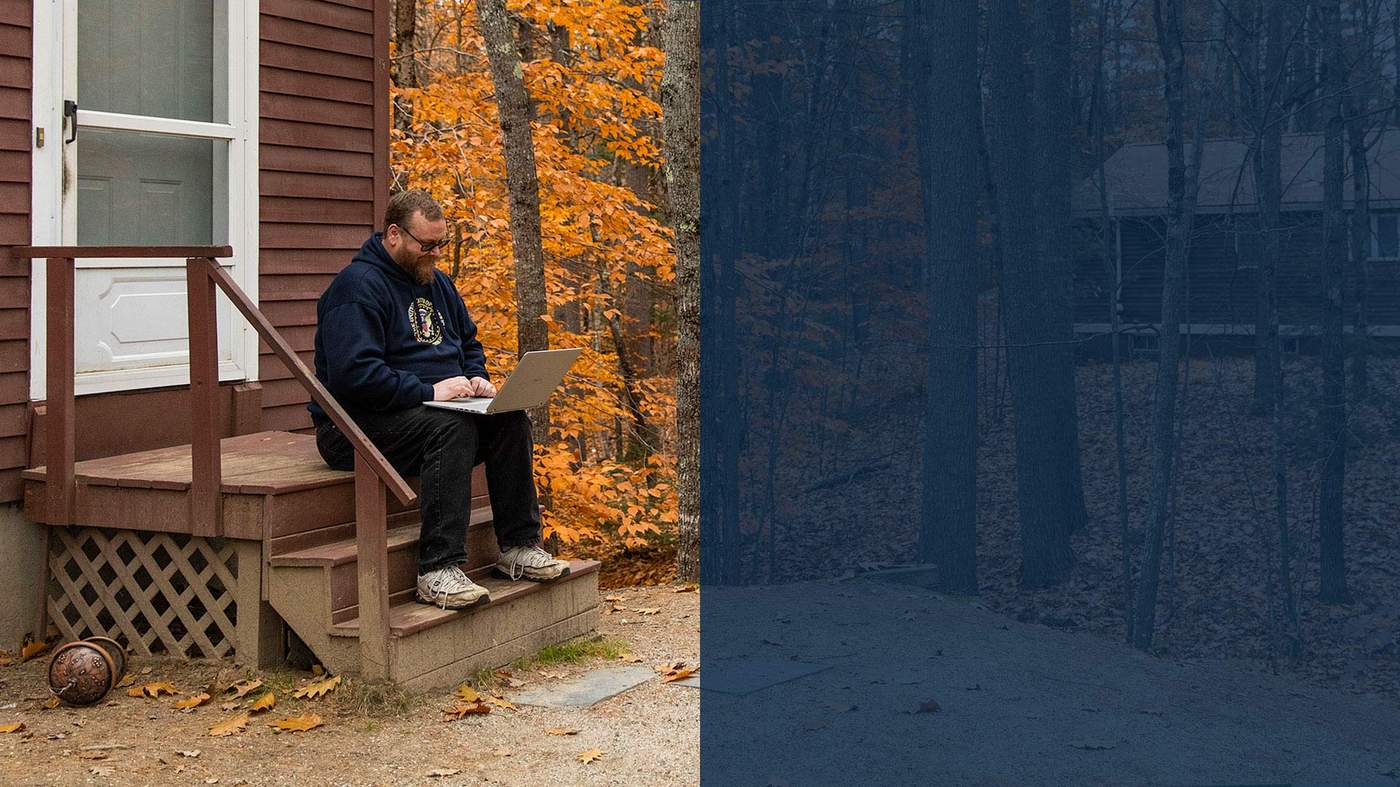
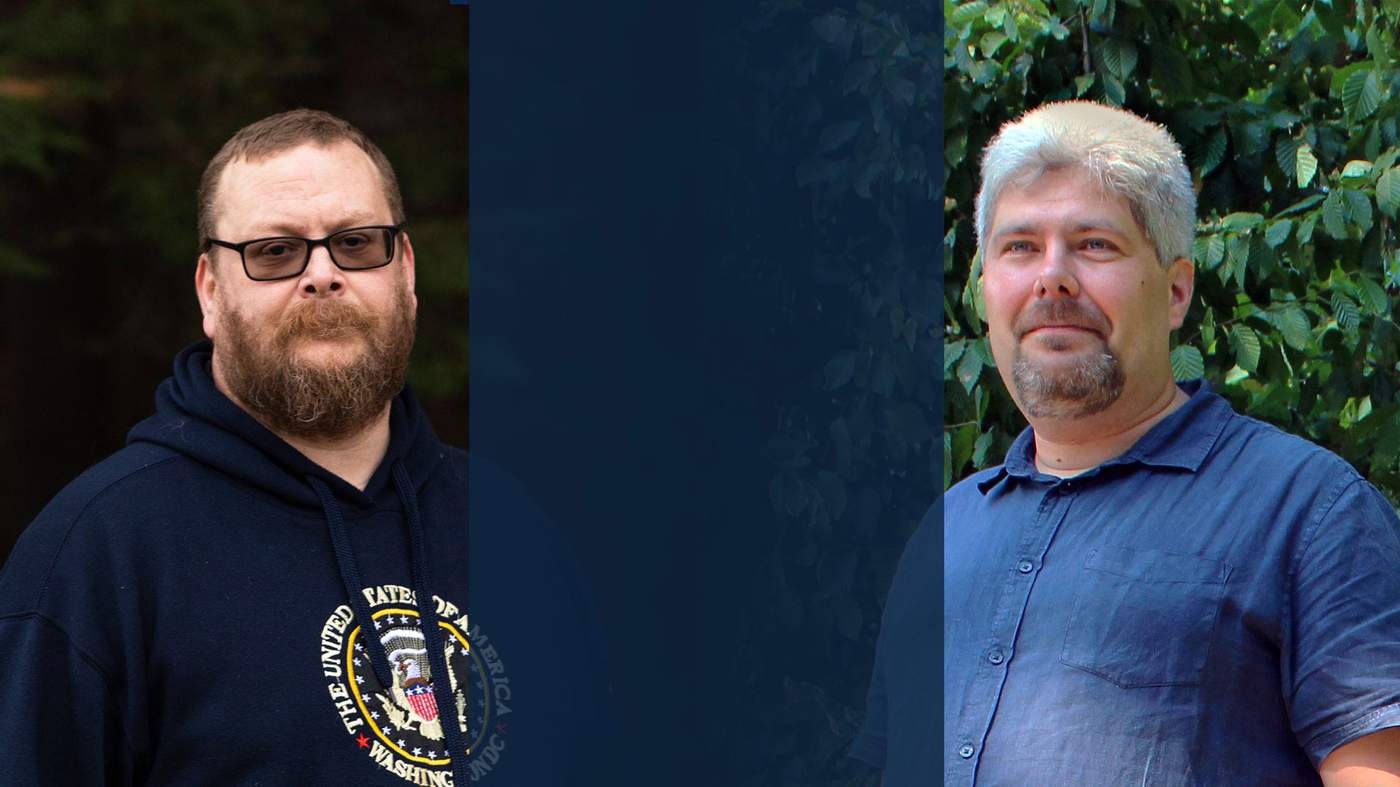
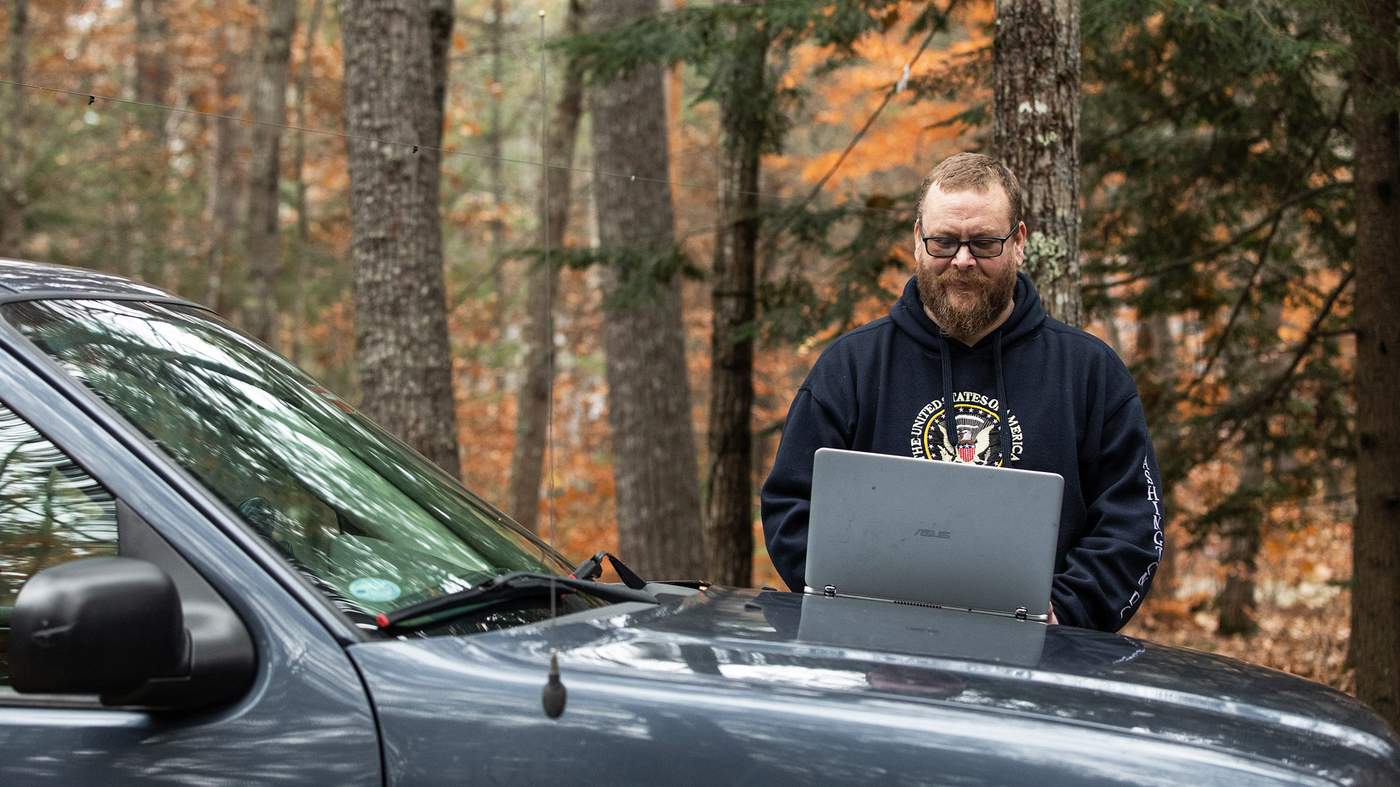
Christopher Blair takes a sip of his coffee.
Then he carefully focuses on one of the three screens in front of him.
He’s in his home office, 45 minutes outside Portland, Maine, on the US East Coast.
Stroking his thick beard, he looks at his bookmarks bar.
He takes another sip before his coffee goes cold, inhales long and hard, then logs into the back end of one of his many websites.
He begins by choosing a subject. Which “lucky” politician will be on the receiving end of his attention today?
Bill Clinton? Hillary Clinton? One of the Obamas?
Or maybe the subject of his story won’t be a person, but a policy. Gun control? Police brutality? Feminism? Anything that will push buttons.


Christopher Blair

Next, the details.
Perhaps he’ll make up a controversial incident, a crime, a new law or a constitutional amendment.
“Changing” the US constitution is particularly fun - he’s already written more than 30 fake amendments. (There are only 27 genuine ones.)
Blair sits back in his chair and focuses intently on the screen. He leans forward, places his hands on the keyboard and starts the same way he does every time.
Caps lock. BREAKING. Colon...

BREAKING: Clinton Foundation Ship Seized at Port of Baltimore Carrying Drugs, Guns and Sex Slaves

The words flow from the thoughts in his head. Unconnected to reality, he needs no research, and no notes.
His fingers rhythmically tap the keys. Letters form into words, words into sentences and sentences into a blog of about 200 words.
It doesn’t take long to write.
Publish.
Blair sits back in his chair and watches the likes and shares roll in.


More than 3,000 miles (5,000km) away in a small town an hour east of the Belgian capital, Brussels, there’s another office in another family home.
Outside, children play in the garden on a warm summer’s afternoon.
Maarten Schenk navigates the steep set of stairs to his basement office. There’s an L-shaped desk in one corner - in another, a cooler is filled with bottles of peach-flavoured iced tea.
His desk resembles Blair’s. On it, sit three computer monitors, with the machine hard drives tucked away neatly underneath.
On one of the screens, he suddenly notices a lot of activity. The US is waking up, and spiking numbers on one page catch Schenk’s attention.
He watches as one particular story is gathering momentum and is quickly being shared on Facebook and other social networks.
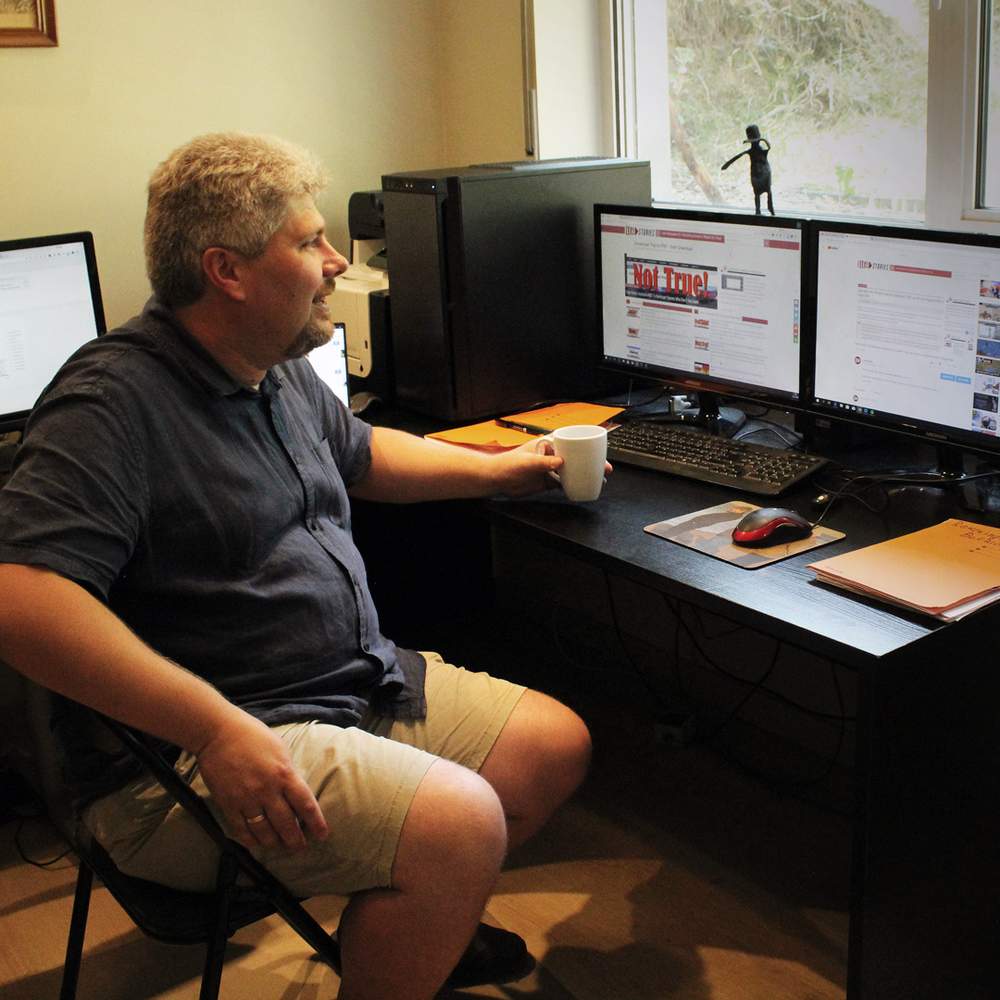


Maarten Schenk

Schenk logs into his own website and starts to type.
His job is to tell the world that what he’s seeing online - the story that’s currently going viral about a Clinton Foundation ship, allegedly carrying drugs, guns and sex slaves - is a complete fabrication.
It’s fake news.


The birth of fake news

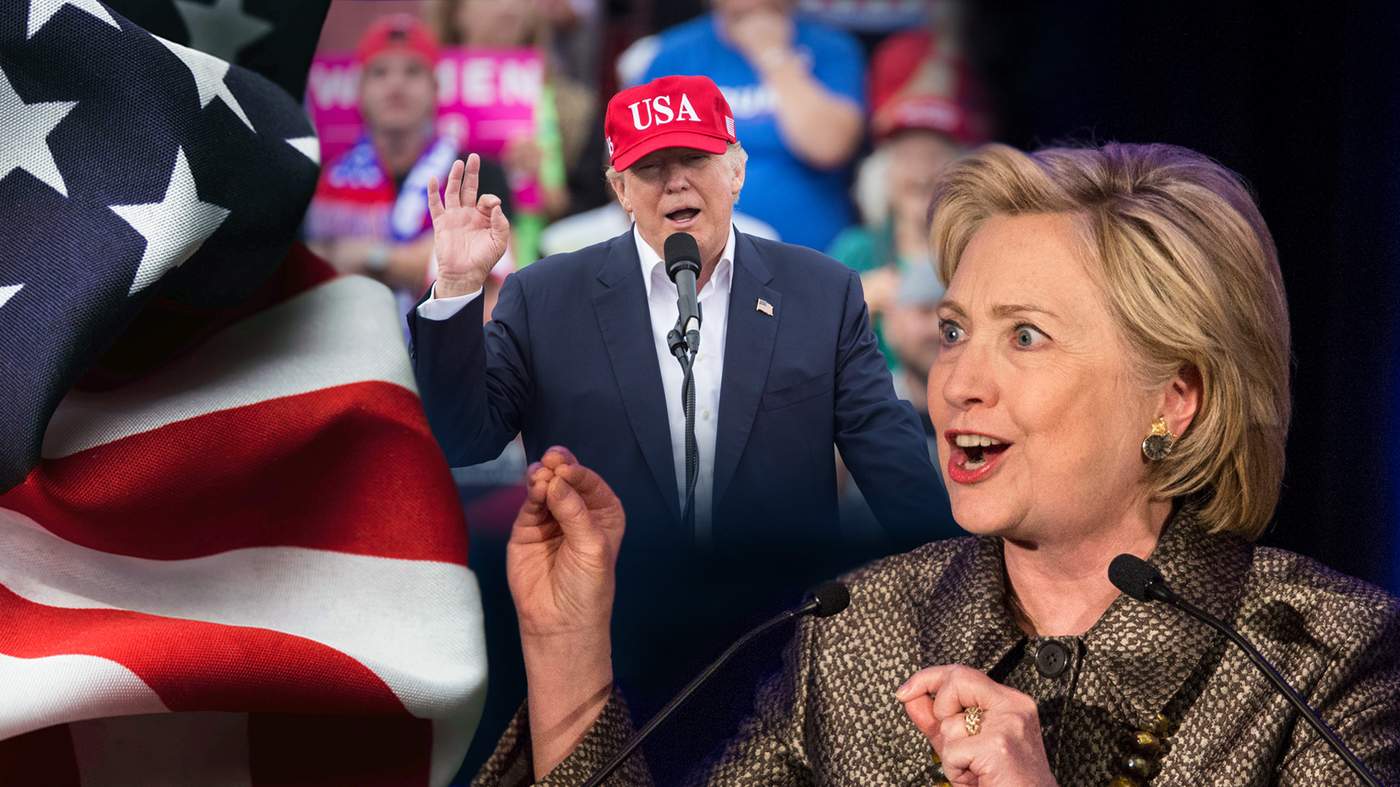
During the 2016 US presidential election, journalists began noticing a rash of viral made-up stories on Facebook.
Bizarrely, many of the pages appeared to be posted by people from the Balkans and, after on an unusual cluster of pages, reporters flocked to a small town called Veles in Macedonia.
“The Americans loved our stories and we make money from them,” one faker told the ����ý. “Who cares if they are true or false?”


The stories were, in the main, pitched to Donald Trump supporters. They included rumours about Hillary Clinton’s health problems and illegal dealings, stories about luminaries like Pope Francis lining up behind the Republican candidate, and other false news sure to either please or rile Trump’s supporters.

It’s now clear that so-called fake news can have real-world consequences

In December 2016, Hillary Clinton gave a speech in which she slammed “the epidemic of malicious fake news and false propaganda” that had flooded social media over the past year.
“It's now clear that so-called fake news can have real-world consequences,” she said.
It wasn’t immediately clear if she was referring to the election. At the time, some journalists interpreted her remarks as a reference to “pizzagate”, a conspiracy theory that grew to tremendous proportions online, and which prompted one man to storm into a Washington DC restaurant and fire an assault rifle.
But regardless of Clinton’s meaning, the term was taken up by her victorious opponent and used in a completely different way a few weeks later.

You are fake news

At a fractious press conference President-elect Trump refused to take a question from CNN reporter Jim Acosta.
“I’m not going to give you a question,” Trump said. “You are fake news.”
Since then, “fake news” has been a topic of mainstream obsession and debate, although what is meant by the term varies hugely.
Some insist on the original definition - fake stories of the type pumped out by those Macedonian teenagers.
Others lump in politically motivated conspiracy theories - perhaps what Hillary Clinton was getting at.



But people have also used “fake news” to describe honest mistakes, opinion, spin, propaganda or - like President Trump - news outlets or reporting that they simply don’t like.
Not only that, but often stuck under the banner of “fake news” is satire or parody, which on the surface appears harmless, but could still fool people - with potentially negative consequences.


‘It will never amount to anything’

Christopher Blair grew up in Lowell, Massachusetts, a city on the northern outskirts of Boston.
His stepfather was a committed Democrat who once ran for the Massachusetts state senate.

Christopher Blair (l)

Blair spent more than two decades as a construction worker, a trade that took a toll on his body. So in the late 2000s, when the Great Recession hit and his industry slumped, he started looking for another source of income in liberal political blogging.
He found he loved to write and had a real flair for making words come alive. He began a blog, the first of many. There was a liberation in being able to say what he wanted - arguing in favour of a range of positions on the left-hand side of American politics.
But although it was fun and a few people started reading, blogging didn’t pay.
And so he tried another tactic. He began to write fabricated, made up tales that looked like real news headlines. Streams of consciousness flowed from his head to the keyboard.
When he saw the results online, the hundreds and thousands of likes and shares his posts were getting, he felt validated. Far more people were interested in fake news than Blair’s opinions or true stories.
Not everyone was convinced.
“You’re wasting all this time,” his wife told him. “It will never amount to anything.”
But once his fake news started to get clicks, he was able to use Google’s advertising platform to convert page views into money. In 2014, he quit his day job completely.
“Once writing became lucrative enough to not destroy my body in construction any more,” he says with a laugh, “that’s when it became time to stay at home with the kids and do this.”
Blair created online identities using pseudonyms and aliases like Busta Troll and Flagg Eagleton.

He took on the personas of patriotic Americans outraged at President Obama, liberals, feminists, the Black Lives Matter movement and more.
He delighted in people who took the lies for the truth and shared the stories as if they came from real news websites.
The success of the fakes led Blair to create a Facebook page called America’s Last Line of Defense. It was dedicated to fake news stories aimed at staunch Republicans and supporters of President Donald Trump.
The headlines were sensational and sometimes even offensive. They had one aim - to provoke an emotional response that would get people to share them.

• BREAKING: Torture Chamber in Bill Clinton’s Basement Described As A ‘Kill Room’
• BREAKING: New Orleans Saints Stranded on Runway in London After Pilot Takes A Knee and Walks Off
• BREAKING: Obama, Soros and the Dems Ordered The Shutdown to Stage A Coup

Blair himself describes the headlines he writes as “racist and bigoted”.
But they went viral, and those shares turned into clicks, which turned into cash.



‘It will never amount to anything’

Christopher Blair grew up in Lowell, Massachusetts, a city on the northern outskirts of Boston.
His stepfather was a committed Democrat who once ran for the Massachusetts state senate.

Christopher Blair (l)

Blair spent more than two decades as a construction worker, a trade that took a toll on his body. In the late 2000s, when the Great Recession hit and his industry slumped, he started looking for another source of income in liberal political blogging.
He loved to write and found that he had a flair for making words come alive. He began a blog, the first of many. He found it liberating being able to say what he wanted - arguing in favour of a range of positions on the left-hand side of American politics.
But although it was fun and a few people started reading, blogging didn’t pay.
And so he tried another tactic. He began to write fabricated tales that looked like real news headlines. Streams of consciousness flowed from his head to the keyboard.
When he saw the results online, the hundreds and thousands of likes and shares his posts were getting, he felt validated. Far more people were interested in fake news than Blair’s opinions or true stories.
Not everyone was convinced.
“You’re wasting all this time,” his wife told him. “It will never amount to anything.”


But once his fake news started to get clicks, he was able to use Google’s advertising platform to convert page views into money. In 2014, he quit his day job.
“Once writing became lucrative enough to not destroy my body in construction any more,” he says with a laugh, “that’s when it became time to stay at home with the kids and do this.”
Blair created online identities using pseudonyms and aliases such as Busta Troll and Flagg Eagleton.

He took on the personas of patriotic Americans outraged at President Obama, liberals, feminists, the Black Lives Matter movement and more.
He delighted in people who took the lies for the truth and shared the stories as if they had come from real news websites.
The success of the fakes led Blair to create a Facebook page called America’s Last Line of Defense. It was dedicated to fake news stories aimed at staunch Republicans and supporters of President Donald Trump.
The headlines were sensational and sometimes even offensive. They had one aim - to provoke an emotional response that would get people to share them.

• BREAKING: Torture Chamber in Bill Clinton’s Basement Described As A ‘Kill Room’
• BREAKING: New Orleans Saints Stranded on Runway in London After Pilot Takes A Knee and Walks Off
• BREAKING: Obama, Soros and the Dems Ordered The Shutdown to Stage A Coup

Blair himself describes the headlines he wrote as “racist and bigoted”.
But they went viral - and those shares turned into clicks, which turned into cash.


The debunking machine

Back in Belgium, computer programmer Maarten Schenk had created software that could detect which stories were trending on Facebook. He called it Trendolizer.
He would then write about them on his blog. But he struggled to find an audience. He was up against some of the world’s biggest media organisations. By the time he noticed a post was trending and wrote about it, big news sites had already covered it.
But like Blair, Schenk discovered a niche when it came to fake news. For all of the people who who liked and shared fictional stories believing them to be real, there were others who appreciated someone who could identify those that were fake.

Just because it’s trending, doesn’t mean it’s true

When he discovered false stories and blogged about them, his site traffic went up. Not by an astonishing amount - he wasn’t making as much money as Blair - but enough for him to concentrate on debunking fake news.
His blog became focused on the fakes, with the tagline: “Just because it’s trending, doesn’t mean it’s true”.
Schenk also noticed patterns and repeated online behaviour. For example, on a weekly basis he saw fake stories about the death of Hillary Clinton.
Every Saturday, he would read that the Democratic nominee had died - in a ballooning accident, boat crash or from a heart attack. Or hit on the head with a monster truck tyre.



As he debunked the fake stories, Schenk began to collect information about fake news websites and the people behind them. His database allowed him to track the fakers across the internet, even as their websites and Facebook pages were taken down.
He noticed broad themes. In addition to Hillary Clinton, voter fraud was a popular subject for fake stories, as were immigration and Islam.
And given the Wild West nature of the fake news world, he increasingly found that more and more sites - including some of those from Macedonia - were stealing content, copy and pasting from other fake news sites.
In fact, many were stealing content from just one source.
That source was Christopher Blair.



A ‘crazy idea’

By early 2017, there was a lot of talk about the rise of Facebook-enabled fake viral news stories. But that didn’t mean that social media companies were doing anything about it.
Facebook chief executive Mark Zuckerberg had famously scoffed at the suggestion that the fakes could sway voters.
“Personally I think the idea that fake news on Facebook... influenced the election in any way - I think is a pretty crazy idea,” he said just after the 2016 presidential election.
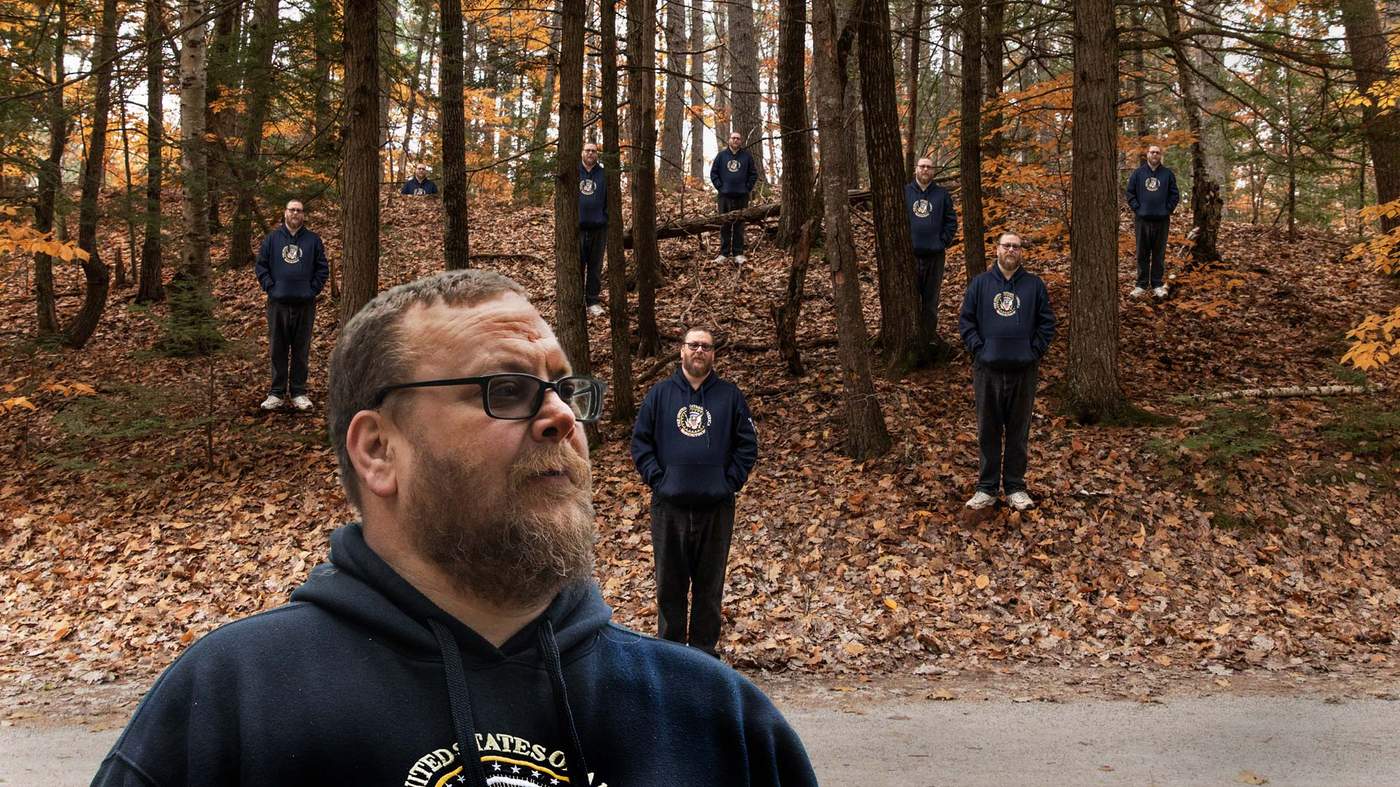
But the frenetic political climate in America meant fake news writers like Blair were more successful than ever before. He hired other writers to churn out the fakes. And the money kept flowing in.
“It was every day, all day,” he says. “We were getting results with what we were doing.”


Christopher Blair and his dog

But the good times couldn’t last forever. The political winds began to turn against him.
Blair, a committed liberal Democrat, was being lumped in with a whole host of people accused of peddling lies to inflate support for President Trump.


Fakers v Fact Checkers

In Belgium, Maarten Schenk was increasingly drawn into the game of cat and mouse.
Fake news writers were finding better, more creative and devious ways to capture an unwitting audience. But at the same time, Schenk was developing his systems, getting better at identifying the fake news writers and, crucially, getting his debunks in front of a wider audience.
“I want to be just a Google search away,” when people think they’re looking at a false story, he says.
Schenk estimates there’s about 200 dedicated fact-checking organisations worldwide - not nearly enough, he says.
“As long as there is potential for profit, people will keep trying,” he says. “People will find new filters and then they [the fake news writers] will find ways to get around the filters.”

Real-world consequences

In August 2017, Hurricane Harvey tore through Texas, killing dozens and causing billions of dollars of damage to Houston and the surrounding areas.
Across the country in Maine, Blair sensed an opportunity to use his creative writing skills.
He made up a story about a fictional imam in a fictional mosque in Texas. The imam, he wrote, refused to shelter non-Muslims during the storm.

He found out, he got really upset... I immediately removed it and sent him a million apologies

It would clearly whip up Blair’s fan base. And it was all untrue. But there was one problem. The photo that was used to accompany the story was of a real imam, the leader of a mosque in Canada.
Ibrahim Hindy had never even visited Texas, but he was suddenly the target of fake news.
“He found out, he got really upset,” says Blair. “He was all over Twitter about how we were racists, xenophobes. The whole nine yards. I immediately removed it and sent him a million apologies.”
It wasn’t the only time that Blair’s falsehoods had snared real people. Another of his websites carried a story about a US soldier who was a deserter. But he used the name and picture of a real person who had nothing to do with the story.
Schenk noticed it going viral. And when he checked it out, he realised that a real person had been unfairly inserted into a fake story.
He messaged Blair and got him to remove the story. But the two men continued messaging online.
And that’s where Blair revealed his secret, his real reason for writing fake news.


Will the real Christopher Blair please stand up?

Blair liked it that Schenk had called him out. There was something that made him stand out from other fact checkers, simply by the fact that he had communicated with him. Other fact-checking websites, he says, write debunking blog posts, but never talk to him before they do.
Schenk stood up to Blair, pointed out the mistake and got the fake story removed from the internet. And so Blair invited Schenk into a secret Facebook group with fans of his work.
It was there that Schenk learnt the truth about Blair, and got an insight into what drove one fake news writer.
“He basically explained his whole schtick,” says Schenk. “How they [fake news writers] work.”
There were heavy hints in the disclaimers that Blair slapped all over his websites and Facebook pages.
The Last Line of Defense has one that reads: “We are here to provide you with information you can use to continue being as informed as a conservative feels comfortable with. Please don't use our page in conjunction with Google or the news, it will only serve to confuse you further.”
Satire - not news, not opinion, and not propaganda - is how Blair describes his work.
His aim is to trick conservative Americans into sharing false news, in the hope of showing what he calls their “stupidity”.



“We’ve gone out of our way to market it as satire, to make sure that everybody knows that this isn’t real,” he says, pointing out that some of his pages have more prominent disclaimers than the world-famous satire site The Onion.
Once his stories go viral, the Facebook comments burst forth. And that’s when Christopher Blair the fake news writer becomes Christopher Blair the crusading left-wing troll.
“The mission with the trolling first and foremost is we pull them into the comments [section underneath each fake article],” he says.
It's then that he starts on the offensive. The faker becomes the exposer, weeding out and reporting the most extreme users among his fans.
“I can show you hundreds of profiles we’ve had taken down,” he says. He claims that he’s exposed Ku Klux Klan members and hardcore racists.
“We’ve had people fired from their jobs,” he says.
“We’ve exposed them to their families. Say what you want about me being a monster. I’m pretty proud.”


Goats on top of goats

Blair and his small army of writers and allies also have other ways of fighting their ideological opponents. And one of his politically motivated stunts has become legendary in the internet world.
“It was a mission that went on for months,” he says.
The goal was to infiltrate conservative Facebook pages and take them over, by winning over the trust of their administrators to the point where they were given admin privileges themselves, which they then used to throw out the original owners.
“There was an army of people involved,” he says, estimating that his group took control of 26 conservative Facebook pages.
“The pictures [originally on the pages] were of Obama being lynched and depicting him as a Muslim. All those stupid hate posts that are on a typical conservative page. We just tore them up, threw them away.
“We took their pages over and replaced everything with pictures of goats,” he says.
“I called the army of trolls and they showed up. For days it was goats on top of goats.”
Schenk knows the story well.
“They called themselves the ‘goatherd’,” he says. The episode was more evidence of Blair’s real motivation - politically motivated pranksterism.


The money dries up

As public awareness about fake viral stories grew, so did pressure on social media companies to do something about it.
Mark Zuckerberg said his personal challenge for 2018 was to “fix” the social site, to combat hate and abuse, but also fake news.
In April, 2018, he was called in front of Congress to answer questions about a host of issues, the fakers on his platform being one of them.
As a result, in July, Facebook announced algorithm changes designed to boost content from “friends, family and groups”. The company, realising it had an image problem, launched an ad campaign to reassure users that they would be protected from “spam, clickbait, fake news and data misuse”.
Some Facebook pages were deleted, while other publishers found that their posts were not travelling as far or as fast as they once had done.

I’m not some monster. I’m a liberal... the goal isn’t money

For Blair, the money began to dry up. Largely because of Facebook’s changes, he says he now makes a fraction of what he did at the height of the fake news boom.
But he insists money was never the motivator, and instead he claims to be a “leader of the resistance” against President Donald Trump and the Republican Party.
“I’m not some monster. I’m a liberal,” he says. “The goal isn’t money.”
“There hasn’t been any money in six months. [But] go look at my page, I’m still active, I’m still doing it. I’m still writing.
“I still believe and I always will.”


Blair and Schenk had swapped messages online, but they’d never actually spoken until recently, when I called them both at the same time and recorded the conversation for ����ý Trending.
They hadn't needed much convincing, and were keen to talk to each other.
But the conversation started awkwardly. Two men who were usually not short of words were suddenly reticent, unsure of what to say.
Schenk began by saying that on one level, he admired Blair.
“He’s very good at what he does,” he says.
“His stories have always been quite easy to debunk because they mostly say, right at the end, it’s all fake - and also [it says the same] in the header of his sites.”
But Schenk will still write about them if they go viral - the fact that something is presented as satire doesn’t stop him from debunking it.
“I see my job as a fact checker. My job is not to give an opinion about it,” he says.

What I do is an art form

“Whether you agree with it or not, what I do is an art form,” Blair says. “The stuff that I write a lot of the time - I read it and I laugh at myself. It’s ridiculous.”
Schenk points out that Blair’s posts often lead him to other fake news writers, ones who don’t use disclaimers and who are much more straightforwardly spreading lies.
The Macedonian teenagers aren’t the only ones copying and pasting from Blair - other fake news writers around the world do the same.
Because of this, Schenk says, “he’s a great way of finding actual fake news sites.”

I’m not trying to shut you down

And so it turns out that a conversation that could have been angry or combative is actually quite friendly. Even when Blair adamantly states he won’t stop writing fake stories.
“I don’t know that [Maarten] wants to close me down. Maybe he does.” Then he speaks directly to his opposite number: “You’re welcome to try,” he chuckles.
“I can most definitely assure you that I’m not trying to shut you down,” Schenk replies.
As the conversation winds down, I ask Blair - this godfather of fake news - and the man who tracked him down, if they have any parting words.
“Don’t ever stop doing what you’re doing,” Blair says.
And, with a hint of respect in his voice, Schenk replies:
“L�����ɾ�����.”











