A couple of weeks back, my colleague Caroline Alton wrote about our work on “Made by Machine: When AI Met The Archive”, our collaboration with ����ý Four to produce an hour of programming, picked from the ����ý’s archive entirely automatically, using machine learning techniques. Creating a TV programme with a minimum of human intervention was an ambitious project, and one without precedent at the ����ý (or, to our knowledge, elsewhere), so I’m going to take some time to outline a bit more detail on the challenges we faced, and the techniques we used to bring this idea to fruition!

����ý R&D has been developing AI to help programme makers and schedulers search the ����ý’s archive, which was being used to help ����ý Four curate an evening of archive programming. As part of this, Cassian Harrison, controller of ����ý Four, asked us to explore what would happen if artificial intelligence then tried to create a programme. This seems like a simple-enough enquiry, but we soon realised it contains interesting subtleties - beyond the practical question of whether it’s possible, there’s also the deeper question of what it might mean for an AI to ‘create’ a programme at all - what constraints would it operate under? What would inform its decisions? What would its objective in creating this programme be?
As the project took shape, some of these questions were answered as a result of the practical constraints of making the programme. We decided early on that the programme should assemble new programmes from archive footage, learning to make decisions from a corpus of the ‘best’ or most representative ����ý Four programmes we’ve produced. This would require us to identify a representative set of ����ý Four programmes, and to segment them into coherent ‘scenes’, for later re-assembly by the ‘AI’.
As an experiment, we tried to do this with as little human intervention as possible, in order to see what was, and wasn’t possible and let people see the results of that. Therefore, we attempted to use machine learning to derive a measure of ‘����ý Four-ness’ which we could use to select the most representative ����ý Four programmes for further processing. We did this by training a linear support vector classifier to predict whether or not a given programme was broadcast on ����ý Four, based on features derived from editorial metadata about that programme (genres, summaries and synopses). This performed very well, with an overall classification accuracy of 97%. We then used this model to generate a score for each programme in our archive (using the distance from the decision boundary as the score), and picked the top 150 programmes for further processing.
The candidate programmes were split into scenes using an algorithm developed by our colleague Craig Wright from ����ý R&D's AI in Production project, while he was on a graduate placement with our own data team, last year. This yielded several thousand individual scenes, which could be stitched back together into new programmes by our machine learning models.
The next question, then, was how to edit these clips back together. It was apparent that there were many approaches we could have taken, based on different algorithms and feature sets, and with very different results. However, this diversity of possible approaches seemed like an interesting opportunity to us - we could use the programme to explore and compare some of these different approaches - highlighting the ways they work (and the ways they fail) in a compelling way for an audience who might not be familiar this sort of technology. In this way, we could produce a programme that wasn’t just made by machine learning, but was about machine learning too - using the task of ‘creating a programme’ to explore some of the wider questions about these technologies and how they make decisions.
Ultimately we chose to concentrate on three approaches to teaching the machine to examine and link footage from across the vast ����ý archive - object detection, subtitle analysis, and ‘visual energy’ analysis, all three of which I’ll explain now.
Our first attempt at analysing the programme segments focused on the visual. We chose to apply the work of Johnson, Karpathy and Li at Stanford University in their paper to analyse the video footage of our programmes and attempt to identify the subjects depicted on screen, via automatic image captioning.

We used these captions to build sequences - starting from a random ‘seed clip’, we would then assemble a sequence by picking clips which depicted a similar scene to the previous one, as determined by our densecap model. This was the first sequence shown in the programme. This produced some interesting results - and also failed in ways which were interesting from a narrative point of view - the machine’s propensity to mis-gender short-haired women, for instance, was an obvious example of the kind of human bias which can be reproduced by machine learning systems. However, this approach really failed to capture much about the narrative subject of our scenes, and didn’t really produce a sequence with overall coherence, leading to our second approach.
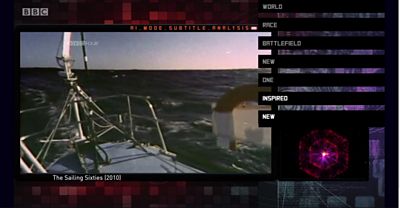
The images on screen don’t tell the whole story in a TV programme - what is on the soundtrack is equally as important to the medium’s ability to tell stories. This is especially true in documentary footage (which made up a large proportion of our corpus of programmes), due to the use of voice-over to drive the overall narrative. As a result, our machine learning models really needed to be able to understand what is said as well as what is shown within our programmes, so this is where we turned our attention for the second section of the programme. Thankfully, the vast majority of our broadcast programmes have already been transcribed (in the form of subtitles), which made this part of the process significantly easier. Using the programme subtitles, we applied various natural language processing techniques including and in order to build a model of semantic similarity between scenes based on their subtitles, and used this to build the second sequence in the programme.
This produced a number of interesting sequences, which to our eyes, appeared to have more thematic coherence than the object-detection approach. The sequence which was selected for the final programme, in particular, to me at least, has rather an interesting thread about British social history running through it - ranging from the Harold Wilson government’s building of the National Theatre, to the philosophical reflections of a Routemaster bus conductor. However, while this produced a promising sequence - we felt that our approaches so far had neglected to incorporate the aesthetic craft of TV storytelling - the way in which moving images and sound are combined to give the impression of specific feelings or sensations, as well as to show images and tell stories. As a result, for our third sequence, we attempted to build a sequence with particular affective properties, rather than a particular coherent story.
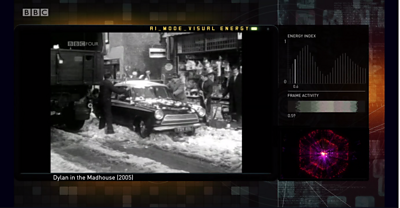
In order to do this, after some discussion with Cassian and the ����ý Four team, we decided to attempt to model the amount of ‘energy’ or ‘dynamism’ in a given scene - the combination of pace of editing, and movement of camera and/or subject which can make a given scene feel relaxing or tense, melancholy or uplifting. We built a model which uses the results of the MPEG-2 video encoding process to rank scenes by their perceived dynamism, then used these ‘visual energy scores’ to map scenes to a ‘narrative curve’ - starting with low energy clips, building to a ‘peak’ of more energetic scenes, before tapering off again. This did indeed produce an interesting analysis of filmic style, and the differences between the high-and-low energy clips seemed pretty apparent (with a couple of exceptions - very grainy, archive film footage, for instance, would consistently be perceived by the machine as ‘high energy’). On it’s own though, this approach doesn’t make for particularly interesting viewing, due to the total absence of any narrative structure to the programme it produces. The question then, is whether we could combine our three approaches into a fourth approach which was greater than the sum of its parts?
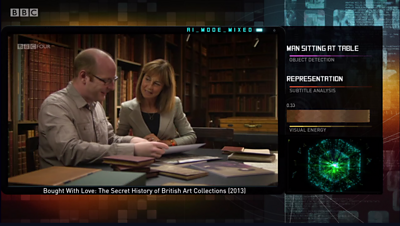
This is exactly what we attempted with the fourth and final sequence in the programme. Using Long short-term memory deep neural networks, and all the feature representations learned by our previous models, we attempted to learn a sequence model from our corpus of ����ý Four programmes - allowing the machine to use all the features we’d derived earlier to learn a sequencing of scenes from the actions of the (human) editors of our archive programmes. At this point the workings of the machine were both un-controllable by its human operators, but also un-interpretable - in complicated neural networks, it’s very difficult to inspect or interpret why certain decisions are made - we could simply sit back and watch, and attempt to interpret the machine’s work, in the same way as the audience of the programme.
So, did this work? in terms of producing compelling television, we’ll let you be the judge of that - at the time of writing, the programme is available to watch on ����ý iPlayer. More generally though, the project was a resounding success in research terms - the techniques and technologies we use have wider application in developing products, services and tools that enable easier access to archive programmes, and the reuse of our archive in new and creative ways, a direction which we are going to continue to explore in the coming months. In addition, having the opportunity to make a TV programme has taught us loads about the TV production process, and given us plenty of ideas for future projects!
- -
- ����ý R&D - AI and the Archive - the making of Made by Machine
- ����ý R&D - AI Opportunities: Transforming Coverage of Live Events
- ����ý R&D - Artificial Intelligence in Broadcasting
- ����ý R&D - ����ý RemArc - how our archives can help people with dementia
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Training and Skills from the ����ý Academy including:
-

Internet Research and Future Services section
The Internet Research and Future Services section is an interdisciplinary team of researchers, technologists, designers, and data scientists who carry out original research to solve problems for the ����ý. ����ý focuses on the intersection of audience needs and public service values, with digital media and machine learning. We develop research insights, prototypes and systems using experimental approaches and emerging technologies.
