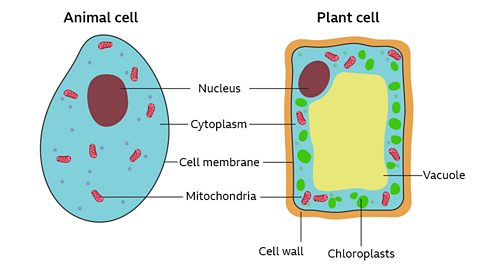
What's in a cell?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all animals and plants.
Inside cells are various structures that are specialised to carry out a particular function. Both animal and plant cells have these components:
- Cell membrane ÔÇô this surrounds the cell and allows nutrients to enter and waste to leave it.
- Nucleus ÔÇô this controls what happens in the cell. It contains DNA, the genetic information that cells need to grow and reproduce.
- Cytoplasm ÔÇô this is a jelly-like substance in which chemical reactions happen.
- Mitochondria ÔÇô these are the powerhouse of the cell. They are structures where respiration takes place.
How are plant and animal cells different?
Plant cells have all the parts in the list above, plus a few extra structures:
- Cell wall - this is an outer structure that surrounds the cell and gives it support.
- Vacuole - this is a space within the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains sap.
- Chloroplasts - these contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis.
How big are cells
Cells can vary greatly in size. You need a microscope to see most human cells.
Red blood cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body. These have a diameter of 0.008mm, meaning a line of 125 red blood cells is only 1mm long.
The ovum (or egg cell) is one of the largest cells in the human body. It has a diameter of roughly 0.1mm, so you can see them without a microscope. A line of 10 egg cells is 1mm long.