Bacterial growth in cultures
bacteriaSingle-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium. can replicate approximately every 20 minutes by binary fission, which is a simple form of cell division. This level of replication will depend on the availability of nutrients and other suitable conditions such as temperature.
There are many ways to culture bacteria, and these include:
- nutrient broth solution in a culture vialSmall glass bottle with lid, often filled with a liquid in which bacteria grow.
- colonies on an agar plate
Nutrient broth solution or culture medium, allows a liquid or gel to provide all the nutrients needed for bacteria to grow successfully. These must include: carbohydrates for energy, nitrogen for protein synthesisThe production of proteins from amino acids, which happens in the ribosomes of the cell., plus other minerals.
agar plateA Petri dish that contains agar gel and usually some nutrients. Agar plates are used to culture (grow) bacteria and fungi in the lab. are created by pouring hot molten agar into sterile Petri dishes, which are then allowed to set. Bacteria can be streaked onto the plates using a loop, and allowed to form individual colonies of the specific bacterium. Alternatively, bacteria can be spread all over the agar plate to form a lawn of bacterial growth, rather than individual colonies.

Nutrient broth solutions, culture vials, agar solution and Petri dishes are all sterilised to stop any other microorganisms growing on or in them. This is often done in an autoclave. These are strong containers, a little like ovens, which use high temperatures and pressures to kill microorganisms.
Personal possessions are swabbed for bacteria which are then cultured on agar plates.
Uncontaminated cultures
If a specific bacterium is going to be cultured or grown, other contaminating bacteria would compete for nutrients in the broth or agar. Plus some bacteria could be harmful (such as pathogenMicroorganism that causes disease.) and would complicate the results of experiments when testing the efficiency of antibiotics or other anti-microbial compounds.
Aseptic technique
To avoid contaminating cultures a special set of processes are used that are called aseptic techniquesName given to the laboratory procedures carried out to prevent the contamination of pure cultures of microorganisms.. This includes:
- killing all microorganisms on equipment such as inoculating loops by flaming equipment in a Bunsen burner or dipping them in alcohol
- keeping all lids on equipment when not in use
- wearing gloves, eye goggles, lab coats or other protective equipment
This avoids contaminating cultures that should already be sterile. The growth medium (broth solutions and agar) will be sterile after autoclaving. The containers (Petri dishes and culture vials) will also be sterile after autoclaving.
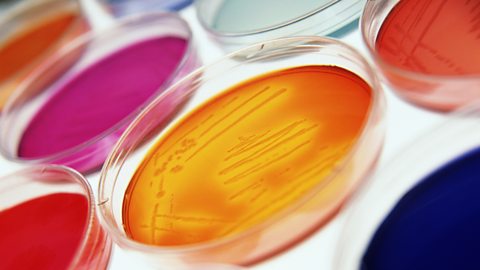
Image caption, Petri dish containing agar on which bacteria are growing
Image caption, Set of culture vials containing broth in which bacteria have grown
1 of 2