Key points
- The productThe result of multiplying one number by another, eg the product of 4 and 5 is 20 since 4 Г— 5 = 20 of two fractions is calculated by multiplying the numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used. Eg, for 1вҒ„3, the numerator is 1 and multiplying the denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts. Eg, for 1вҒ„3, the denominator is 3.
- The word вҖҳofвҖҷ can be replaced by вҖҳmultiplied byвҖҷ as it means the same thing. For example,\( \frac{1}{2} \)of\( \frac{1}{3} \)is the same as \( \frac{1}{2} \)multiplied by \( \frac{1}{3} \)
- Sometimes the calculation can be simplified before multiplying.
- mixed numberA number that is written using a whole number and a fraction, eg 3 4вҒ„5 must be converted to improper fractionA fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator, eg 9вҒ„4 before multiplying.
How to multiply fractions
To multiply fractions:
Multiply the numerators.
Multiply the denominators.
Simplify the answer.
The answer may be simplified before calculation using the highest common factor (HCF) The largest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. Eg, 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20. Highest common factor is written as HCF.
Examples
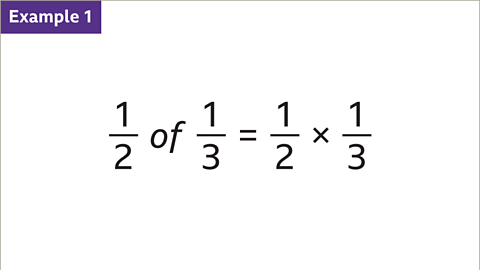
Image caption, 1вҒ„2 of 1вҒ„3 is the same as 1вҒ„2 multiplied by 1вҒ„3. Work out 1вҒ„2 of 1вҒ„3
Image caption, Diagrams can be drawn to illustrate this calculation. Draw a rectangle. Split the width into halves. Split the length into thirds. The rectangle is now split into 6 parts (sixths).
Image caption, 1вҒ„2 of 1вҒ„3 is 1вҒ„6. The product of 1вҒ„2 and 1вҒ„3 is 1вҒ„6 (1вҒ„2 Г— 1вҒ„3 = 1вҒ„6)
Image caption, Multiplication can be processed in either order. 1вҒ„2 multiplied by 1вҒ„3 is the same as a 1вҒ„3 multiplied by 1вҒ„2. The rectangle can be used in either orientation. The answer is 1вҒ„6
Image caption, Work out 3вҒ„4 multiplied by 1вҒ„2
Image caption, To work out 3вҒ„4 Г— 1вҒ„2, draw a rectangle. Split the length into quarters and the width into halves. The rectangle is now split into 8 parts (eighths). 3вҒ„4 x 1вҒ„2 = 3вҒ„8
Image caption, To work out 4вҒ„5 Г— 3вҒ„8, multiply the numerators (4 x 3 = 12) and multiply the denominators (5 Г— 8 = 40). This gives the answer 12вҒ„40, which can be simplified to 3вҒ„10. This calculation can also be simplified before multiplying.
Image caption, The multiplication calculation can be simplified when both a numerator and a denominator have a HCF greater than 1. The HCF of 4 and 8 is 4
Image caption, Divide 4 and 8 by their HCF (4). The calculation has been simplified to 1вҒ„5 multiplied by 3вҒ„2
Image caption, 1вҒ„5 Г— 3вҒ„2 gives the same answer as 4вҒ„5 Г— 3вҒ„8. The simplifying has been done first to make the calculation easier. 4вҒ„5 Г— 3вҒ„8 = 3вҒ„10
1 of 10
Question
Find the product of\( \frac{2}{9} \)and\( \frac{4}{5} \)
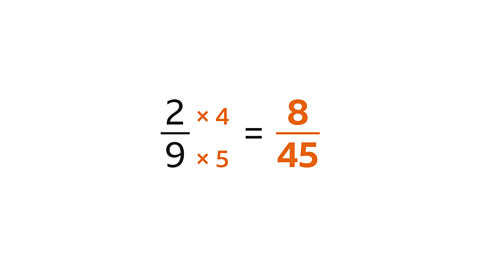
To find the product of the fractions, multiply the numerators (2 and 4) and multiply the denominators (9 and 5). The product is\( \frac{8}{45} \)
How to multiply mixed numbers
To multiply mixed numbers:
Rewrite the mixed numberA number that is written using a whole number and a fraction, eg 3 4вҒ„5 as improper fractionA fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator, eg 9вҒ„4. This is done by multiplying the integer by the denominator and adding the numerator.
If possible, simplify before calculating using the highest common factor (HCF) The largest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. Eg, 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20. Highest common factor is written as HCF.
Multiply the numerators.
Multiply the denominators.
Simplify the answer if possible.
Examples
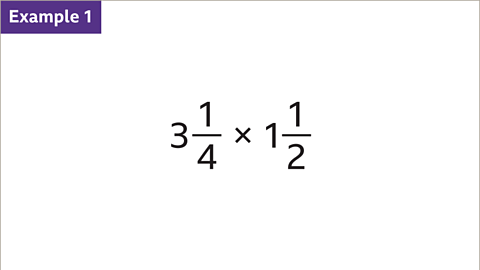
Image caption, Multiply 3 1вҒ„4 by 1 1вҒ„2
Image caption, Convert each mixed number into an improper fraction. The calculation becomes 13вҒ„4 Г— 3вҒ„2
Image caption, Multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators.
Image caption, The improper fraction can be written as a mixed number. 39вҒ„8 is 4 7вҒ„8
Image caption, Multiply 2 7вҒ„10 by 4 1вҒ„6
Image caption, Convert each mixed number into an improper fraction. The calculation becomes 27вҒ„10 Г— 25вҒ„6. This can be simplified.
Image caption, The HCF of 27 and 6 is 3. The HCF of 10 and 25 is 5. Divide by these factors.
Image caption, The calculation has been simplified to 9вҒ„2 Г— 5вҒ„2
Image caption, 9 x 5 = 45. 2 x 2 = 4. 45вҒ„4 is 11 1вҒ„4 as a mixed number.
1 of 9
Question
Find the product of \( 3\frac{1}{4} \) and \( 2\frac{2}{3} \)
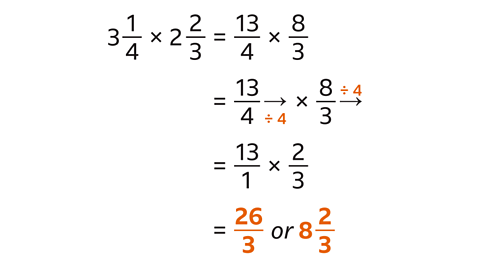
Convert the mixed numbers into improper fractions.
Simplify the calculation by dividing a numerator and a denominator by their highest common factor (4)
Multiply the numerators (13 and 2) and multiply the denominators (1 and 3)
The product is \( \frac{26}{3} \) which is \( 8 \frac{2}{3} \)as a mixed number.
Practise multiplying fractions
Try this quiz to practise multiplying fractions. You may need a pen and paper to solve some of these problems.
Quiz
Real-world maths

In genetics (the study of how genes and characteristics are passed down), multiplying by fractions can help track and predict the likelihood of features being passed onto a child, such as freckles or hair colour.
Half of a childвҖҷs genes come from one parent and half from another. When both parents carry the gene for a particular feature, they each have a chance of passing this on to the child.
By multiplying fractions, the chance of the child inheriting that feature can be worked out. For example, if both parents have\( \frac{1}{2} \)a chance of passing a feature on, the likelihood of inheriting is\( \frac{1}{4}\).

Game - Divided Islands
Play the Divided Islands game! gamePlay the Divided Islands game!
Using your maths skills, help to build bridges and bring light back to the islands in this free game from ҙуПуҙ«ГҪ Bitesize.

More on Fractions
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 14
- count10 of 14
- count11 of 14
- count12 of 14
