ZACH: Our virtual skateboard is looking awesome, Kayla!
KAYLA: Yeah, but I think we should add in some more ramps.
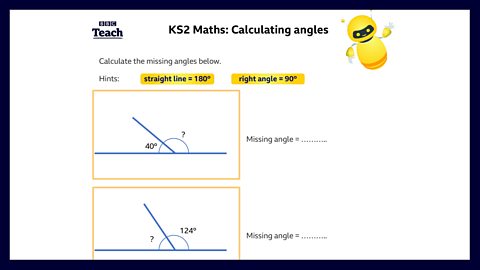
ZACH: LetÔÇÖs have a look at our design.Ah, one of the angle measurements is missing on this one.How do we work it out, Ada?
ADA: You can see that the angles are on a straight line.We know that a straight line is 180 degrees.
KAYLA: So, we know both angles must add up to 180 degrees.
ZACH: And it says this angle is 125 degrees.So, the ramp angle must be 180 minus 125which equals 55 degrees.
ADA: Yes. You can make sure you have the right answer by adding 125 and 55, and checking that they add up to 180 degrees.
KAYLA: 125 + 55 = 180.Nice!Whoa! That ramp is really steep.
ZACH: DonÔÇÖt you mean really scary?IÔÇÖve got a design for a more mellow ramp here.Oops! WeÔÇÖre going to have to move that house out of the way though.
ADA: Not so fast, skater boy!We can use the house to help us find the angle of the ramp.Look. The edge of the house forms a right angle with the ground.Do you remember how many degrees in a right angle?
KAYLA: 90 degrees, right?
ADA: Precisely.We know these angles must add up to 180 degrees because the ground is a straight line again, and this angle is 90 degrees.How can you calculate the missing angle?
ZACH: If we add 90 + 63, that makes 153.
KAYLA: And then, if we subtract 153 from 180, that equals 27.The angle of the ramp is 27 degrees.LetÔÇÖs build it.
ADA: Weeee!!Ouch!Did you forget something?
ZACH: Sorry, Ada!There Deleted.
KAYLA: Hmm, you know what our skatepark needs?
ZACH: What?
KAYLA: My second favourite thing after skatingPizza!We can make a pizza van.
ZACH: Oh yes! LetÔÇÖs make some pizzas.My favourite one has four sections with four different toppings.Like this.
KAYLA: Looks yummy!
ADA: It looks like a good way to learn about angles around a point.Zachs whole pizza is a full turn: 360 degrees.And each section
KAYLA: Ah! Each section is a right angle.90 degrees each.
ADA: ThatÔÇÖs right.How about this pizza which is split into three sections.Can you work out the angle of the pepperoni slice?
ZACH: Hmm so, this angle is 139 and this angle is 153.If we add them up, it equals 292 and the whole turn is 360.
KAYLA: So, to find the missing angle, we subtract 292 from 360, which equals 68 degrees of tasty pepperoni.
Right, Ada?
ZACH: Where did she go?
[ADA CLEARS THROAT]
ADA: Excuse me.Just doing some virtual city testing duties.
This episode moves on from measuring angles to calculating angles on a straight line and full turn.
Zach and Kayla want to add some more ramps to their virtual skate park. They discover that one of the angle measurements on their design is missing, and Ada teaches them to work out the missing angle by subtracting the given angle from 180┬░.
She then teaches them to check their answer by adding the two angles and checking that they equal 180┬░. They repeat this with another ramp, this time including a right angle. A bar model is displayed to show how the three angles add up to 180┬░.
Zach and Kayla decide to add a pizza van to their virtual city. Ada uses this opportunity to teach them how the angles around a full turn add up to 360┬░, and how to find a missing angle by subtracting given angles from 360┬░.
This short animated film is from the ┤¾¤¾┤½├¢ Teach series, Neon City: Measurement and Geometry.
Download/print an A4 activity sheet for this episode (PDF, 204KB). See link below for answers.
Teacher notes
Before watching
You might want to ensure that children are confident with measuring angles.
It would be helpful if they are secure in their knowledge of the types of angles, and know that a right angle equals 90 degrees, a straight line is equal to 180┬░ and a full turn is equal to 360┬░. You also may want to recap methods for mental subtraction to ensure that children can confidently subtract from 180 and 360.
During the film
You might want to stop the film at appropriate points to check for understanding. As Ada asks Zach and Kayla to work out the missing angles, you could pause the film and ask your pupils to do the working themselves, and explain clearly how they got to their answer. Is there more than one way to work these out?
You could ask the pupils to draw a bar model similar to the one displayed on the screen, to show how the angles add up to 180┬░, or 360┬░.
After watching
You could provide the children with more examples of missing angle questions, on a straight line and around a full turn. Can they check their answers using the method taught in the film?
You could ask the children to draw their own examples of angles on a straight line or around a point, using a protractor, and then give to a partner to calculate the missing angles without using a protractor.
(PDF, 690KB)
Curriculum notes
This short film is suitable for teaching maths at KS2 in England and Northern Ireland, 2nd Level in Scotland and Progression steps 2 and 3 in Wales.
More from Neon City: Measurement and Geometry
Measuring area. video
Ada introduces Zach and Kayla to the concept of area, and different ways to measure and calculate the area of rectangles, triangles and composite shapes.

Perimeter. video
Zach and Kayla are creating windows for their virtual house design and Ada explains how they can work out the perimeter for the windows they want.
Volume. video
Kayla and Zach decide to build a swimming pool for their virtual city and Ada explains how to calculate the volume and capacity of a cuboid shape.

Metric and imperial measurements. video
Kayla and Zach decide to build a new hovertrain system from the city to the beach, but they get confused between kilometres and miles. Ada explains how to calculate betwen the two measurement systems, metric and imperial.

Measuring angles - Part 1. video
Kayla and Zach are designing ramps for the skatepark and Ada explains that designing ramps requires us to measure angles ÔÇô the amount of turn between two lines.
Missing lengths and angles. video
A computer virus has corrupted the Neon City software. Zach and Kayla must answer four questions within three minutes, or their city will be erased.

Regular and irregular polygons. video
ZachÔÇÖs design for a pond in the virtual city park leads to Ada explaining the properties of regular and irregular polygons.

Coordinates on a grid. video
Kayla and Zach are designing a fairground and need to plot where to place the different rides, so Ada teaches them about the x-axis and y-axis on a coordinate grid.

Units of time. video
Ada asks Kayla and Zach a series of quiz questions, requiring them to convert from one time measurement unit to another.
