Key points
- Specialised animal cells have components that allow them to complete a specific purpose.
- Specialised animal cells include red blood cells, sperm, eggs, nerve cells, muscle cells, ciliated cells, and villi.
Video - What are specialised animal cells?
Did you know learning about animal cells can be a real lark?
Get it, lark? Anyone? Okay let's move on.
An animal cell is made of three main parts a nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm, which holds the rest of its critical components. And it's so small you could actually fit 100 animal cells across the width of a tiny full stop.
To help animals do all the peculiar things that they, or should I say, we can do there are many specialised cells.
Red blood cells for example, have no nucleus, so they can hold more oxygen. They're also biconcave or disc-shaped to absorb oxygen more quickly and rounded to flow easily through tiny capillaries.
Sperm cells can swim fast thanks to a tail, streamlined shape and a high concentration of energy transferring mitochondria. Good thing too, because without sperm, animals couldn't reproduce.
Muscle cells are full of long protein filaments that can slide past each other to contract the muscle, making it possible for animals to swim, fly or run.
Alright time for this animal to run. Ciao!
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. What are the three main components of animal cells?
2. How many animal cells could fit across the width of a full stop?
A nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm
100
Most cells share features such as having a nucleus, a cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria.
Each type of cell has its own job to do. These cells have special features that allow them to perform their functions effectively.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells carry oxygen around the body, which is needed for respirationA chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria of cells in which glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy.They are well suited to this function because:
- They contain haemoglobinThe chemical in red blood cells in which oxygen binds to be carried from the lungs to the rest of the body., which carries oxygen molecules.
- They don't have a nucleus, allowing more space to carry oxygen.
- They are a flat disc shape with dips on both sides (biconcave). This gives them a large surface area, and the best chance of absorbing as much oxygen as they can in the lungs.
Sperm cells
Sperm are the male sex cell. They are made in the testes after pubertyThe time that a teenager becomes sexually mature and physically able to have a baby.. They join with an egg cell during fertilisationThe joining of male and female gametes (sperm and ova or eggs). to form an embryoA bundle of several hundred cells that has developed from a fertilised ovum. which can then develop into a new life. The following features make them well suited to this function:
- A tail moves them towards an egg cell.
- Many mitochondriaTiny parts of cells floating in the cytoplasm where energy is released from glucose. The glucose comes from food. release energy for movement.
- Part of the tip of the head of the sperm, called the acrosome, releases enzymes to digest the egg membrane to allow fertilisation to take place.
- The haploidA cell which contains half the number of chromosomes compared to other cells in the organism. Eg gametes. nucleus contains the genetic material for fertilisation.
- Sperm are produced in large numbers to increase the chance of fertilisation.
Egg cell
Eggs are the female sex cell. They are made in the ovaries before birth. Usually, one egg is released each month during the , but sometimes this number may be higher. They join with a sperm cell during fertilisation to form an embryo which can then develop into a new life. They are well suited to this function because:
- The egg cellÔÇÖs cytoplasm contains nutrients for the growth of the early embryo.
- The haploid nucleus contains genetic material for fertilisation.
- The cell membraneThis surrounds the outside of animal cells and controls what can enter and exit it. changes after fertilisation by a single sperm so that no more sperm can enter.
Nerve cells
Nerve cells transmit electrical signals in the nervous systemBody system that includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves.. They are well suited to their function because:
- They are thin, and can be more than one metre long in your spinal cord. This means they can carry messages up and down the body over large distances very quickly.
- Nerve cells have branched connections at each end. These join to other nerve cells, allowing them to pass messages around the body.
- They have a fatty (myelin) sheath that surrounds them. The fatty sheath increases the speed at which the message can travel.
Muscle cells
Muscles cells are found in bundles which make up our muscles. These cells are able to contract (get shorter) and relax (return to original length). There are different types of muscle cell, each perfectly adapted to its function:
- Cardiac (heart) muscle cells contract and relax to pump blood around our bodies for our entire lives. They never get tired.
- Smooth muscle cells make up thin sheets of muscle, such as the stomach lining. They can also be arranged in bundles, or rings, like that in the anus.
- Skeletal muscle is joined to bones. Its cells contract to make bones move and joints bend.
Video - Understanding muscle cells
Find out how a sports therapist uses his knowledge of specialised cells to help his clients
It's really important to know about different types of muscle cells because this allows us to understand how to best use them. I'm Ruben Tabares, strength and conditioning coach, nutritionist and sports therapist. My job is to make people stronger, faster - to make them healthier.
Specialised cells are cells designed to carry out a particular role in the body, such as red blood cells which are designed to carry oxygen. Nerve cells help contraction of muscles or the relaxation of muscles according to what specific job you need them to do. The type of muscle that helps with digestion is called smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle pumps blood around the body. Skeletal muscle is made out of specialised skeletal muscle cells.
It's not all about having big muscles. I personally like everyone I work with to have muscle fit for purpose. There's absolutely no difference between an elite level sports person, such as Usain Bolt, as opposed to a person who's never really trained before. If they're both running, they're using these same muscles. The only difference is, someone like Usain Bolt, they've trained their muscles over a longer period of time and when they push, they have more power in their muscles.
It's really important to keep our muscles healthy because we want to be able to do the same things when we're young as when we're old. By having strong muscles, you ensure that as you get older you can still run, you can still walk up and down the stairs. You can do all of the things that you did when you were younger.
The best thing about my job is watching people achieve their goals. I do that with many different athletes across many different sports, and that is for sure the best thing about my job.
Ciliated cells
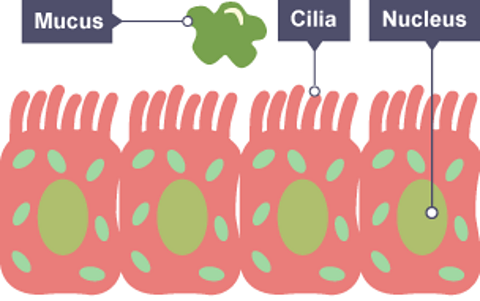
Ciliated cells are found in the airways. They have tiny hairs on their tops called ciliaThe tiny hairs found on the top of ciliated cells which beat. which beat in a rhythm. These hairs move mucus containing dust and other particles upwards and out of the airways. Ciliated cells are also found in the oviductsTubes in the female reproductive system which join the two ovaries to the uterus. Also called fallopian tubes.. Here the tiny hairs beat to move the egg from the ovaries to the uterusThe part of the female reproductive system where a fertilised egg cell develops into an embryo and then a fetus. Also called the womb..

Villi
Villi are structures about one millimetre long in the small intestinesThe part of your digestive system in which digested food is absorbed into the blood. and large intestinesThe part of your digestive system in which water from food and drink is absorbed into the blood.. Millions of them poke out to absorb digested food and water into the blood. They are well suited to this function because:
- They have a large surface area.
- They have thin walls which are only one cell thick.
- The cells of the lining have tiny hairs to absorb more food and water.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
What are the adaptations of red blood cells?
- Red blood cells contain haemoglobin, which carries oxygen molecules.
- They don't have a nucleus, allowing more space to carry oxygen.
- They are a flat disc shape with dips on both sides (biconcave) which gives them a large surface area.
What are the adaptations of nerve cells?
- Nerve cells are thin and long so they can carry messages all over the body very quickly.
- They have branched connections at each end to allow electrical signals to pass to other cells.
- They have a fatty (myelin) sheath that surrounds them and increases the speed at which the electrical signal can travel.
Teaching resources
Looking for even more teaching resources to engage your students? This series of short films introduces the key concepts in Biology, exploring wildlife and the natural world.
┤¾¤¾┤½├¢ Teach has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Living organisms
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 15

- count4 of 15
- count5 of 15
- count6 of 15
