Games
Game - Atomic Labs
Get hands-on with science investigations in Atomic Labs. Experiment and put your science skills to the test using Bunsen burners, test tubes and much more.

Living organisms
Animal and plant cells
Find out about the cell components that are found in both animal and plant cells.

Specialised animal cells
Discover the different types of cells found in animals and what their role is. Learn about nerve cells, ciliated cells, muscle cells and more.

Specialised plant cells
Discover the different types of cells found in plants, and what each one does. Learn about xylem cells, phloem cells, root hair cells and more.

The four components of the blood
There are four parts of the blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma and platelets.
The skeletal system
Learn about the skeleton, a system of bones and joints that has many important jobs, such as protecting organs and helping the body to move.
Skeletal muscles
Learn about the muscles that work together in pairs to move the bones and body. Discover which muscles, bones and joints are involved in kicking a ball or raising an arm.

Biomechanics
Learn how the skeleton moves at its joints with help from muscles, including examples of hinge, pivot, and ball and socket joints.

Adult and embryonic stem cells
There are two types of stem cells in humans: Embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Find out about the differences between them.
How plants and animals are organised
Cells in animals and plants are arranged into tissues, organs and organ systems.

Leaf structure
Learn about the structure and function of leaves.

Unicellular organisms
Find out about unicellular organisms - a living thing that is made of just one cell.
Cellulose
An explanation of what cellulose is and how it is used.

The role of diffusion in and within cells
Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low areas of concentration. Learn how cells use it to transfer substances.

How to make a model animal and plant cell
Animal and plant cells can be visualised using a model. Find out how to make them.

How to observe cells under a microscope
Discover how to observe cells using a microscope.

Nutrition, digestion and excretion
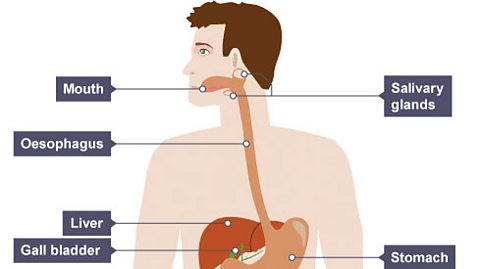
Structure of the digestive system
The digestive system is made up of key parts, each of which has a different function.
Digestive enzymes and absorption
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions including digestion.

Food energy
Food is a store of energy, transferred from the food to the consumer.

Healthy diet
A balanced diet contains the correct amount of all food groups.

Malnutrition
There are two types of malnutrition: when and how do they occur?

Obesity
'Obese' is a medical term used to describe a person with a high excess of body fat.

Lipids, oils and fats
Lipids include fats (solid at room temperature) and oils (liquid at room temperature).

Vitamins and minerals
Vitamins and minerals help the body to use other nutrients efficiently.

Protein
Proteins are a vital part of a healthy diet. Protein-rich foods include fish, meat, eggs and beans.

Dietary fibre
Dietary fibre is plant material that cannot be digested by the human body.

Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy in a healthy diet. Starchy and sugary foods are high in carbohydrates.

Starch
Starch is a type of carbohydrate. Its molecules contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.

What is poo?
Poo (faeces) is the waste that remains after food has been digested and its nutrients absorbed by the body.
Modelling the digestive system
Try this experiment and recreate processes in the digestive system with online and lab options.
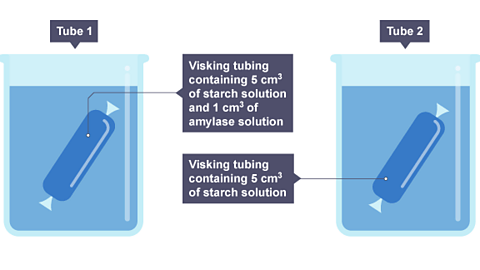
How to model digestion using tights
Learn how digestion works and how to model digestion using a pair of tights.

Respiration and gas exchange
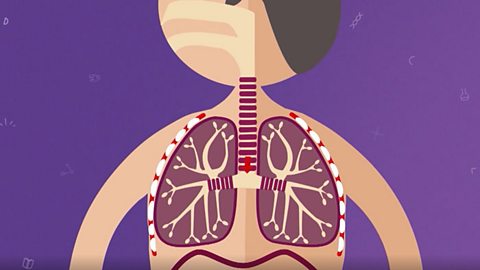
Structure and function of the gas exchange system
The human body takes in oxygen and lets out carbon dioxide. Many parts of the body are involved, including the lungs, airways and blood.

Respiration
Respiration is a chemical reaction which occurs in all living cells, releasing energy from glucose.

The process of breathing
Breathing is also called 'ventilation' and is the movement of gases into and out from the lungs.
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and releases less energy but more quickly than aerobic respiration.

Lactic acid
Lactic acid is the waste product produced during anaerobic respiration.

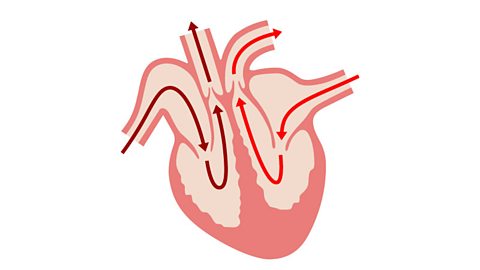
The circulatory system
The circulatory system is the heart and all the blood vessels in the body which carry cells and substances to all its parts.
The effect of asthma, smoking and exercise on the gas exchange system
The gas exchange system is the parts of the body involved in breathing, such as the lungs, airways and diaphragm. Different conditions and activities affect this system.

Glucose
Cells get the energy they need from glucose during respiration. Watch a visual explanation of glucose.

Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that takes place inside a plant, producing food for the plant to survive.

Photosynthesis and respiration in plants
Photosynthesis and respiration are processes that allow plants to make food and release energy.
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis in crop growing
Temperature, light intensity and carbon dioxide are just some of the factors that affect photosynthesis. These factors can be manipulated to maximise growth.

Investigating the rate of photosynthesis
Try this experiment and use pondweed to see how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis.
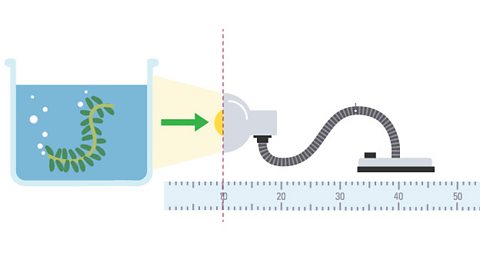
How to measure your lung capacity
The maximum amount of air you can breathe in and out is your vital lung capacity. This experiment shows how this can be measured.

Health and disease
The effects of recreational drugs on health and behaviour
Legal and illegal drugs can change how people act and cause health problems.

Human illnesses
Learn about communicable diseases and non-communicable diseases - in other words, those that can be spread and those that can't.

How antibiotics and vaccines work
Learn how vaccines and antibiotics work in different ways to protect against illness.
Mental health
Learn about the causes and effects of common mental health issues such as stress, anxiety and depression.

Should sugary drinks be banned for under-18s?
Discussing whether we should ban sugary drinks for under 18s. Can you think like a scientist?

Reproduction
Human reproduction
Learn about the cells and body parts involved in reproduction, how a baby grows in the uterus, and what happens at birth.

Fertilisation
Learn about sperm and egg cells, and find out how a baby grows in the uterus.
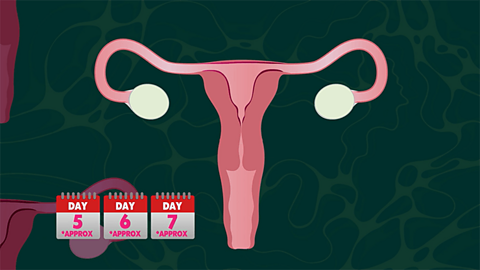
Changes that occur during the menstrual cycle
The effects of the menstrual cycle can be different for each person, but here are some of the ways it can change the body.
Flowers and pollination
Flowers reproduce through a process called pollination. Different flowers spread their pollen grains in different ways including using pollinators.

Fruit and seeds
Fruit and seeds help plants to reproduce. Plants spread their seeds through wind, water, animals and explosions.

Ecosystems and habitats
Food chains and webs
All organisms in an ecosystem depend on each other. Food chains show the flow of energy from one organism to another.

Changes to food webs
All organisms in a food web depend upon each other and changes to one can affect the others.

Ecological sampling
Sampling is the process of looking at part of a population or habitat to draw conclusions about the whole thing. Learn how sampling is used to find out about animals and plants.

Pyramids of number and biomass
Pyramids of numbers and biomass are different ways of showing the amount of organisms at each stage in the food chain.

Kingdoms and classifications
Learn how different species group together and how they are related to each other.

Adaptations of plants
Plants live in a wide variety of habitats. Learn how each species is adapted to suit where they live.

Biodiversity, gene pools and extinctions
Biodiversity is a measure of the range of living organisms within a habitat. A gene pool is the range of DNA in a species.

Inheritance and genetics
DNA
DNA is the genetic code which makes up genes, which are responsible for giving an organism a specific characteristic.

Causes of variation
Some variation is passed on via genes and some variation is the result of differences in the surroundings, or what an individual does.

Types of variation
Collecting data on the differences between members of a species can give two different types of results: continuous and discontinuous.

Inheritance
Characteristics like eye colour and genetic diseases are inherited.

Adaptations and evolution
Evolution explains how better adapted organisms have an advantage.

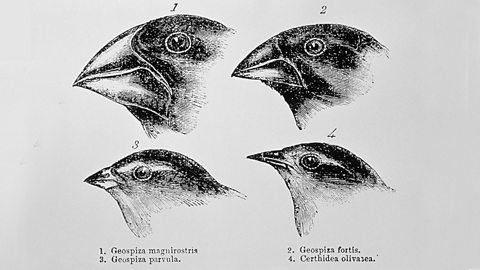
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is known as вҖҳthe survival of the fittestвҖҷ. The best adapted organisms are able to survive.

Natural selection leads to evolution
Evolution is the process by which small changes in organisms occur over long periods of time and new species are formed.
Species and selective breeding
Selective breeding is when organisms are deliberately bred so their offspring have the desirable characteristics.

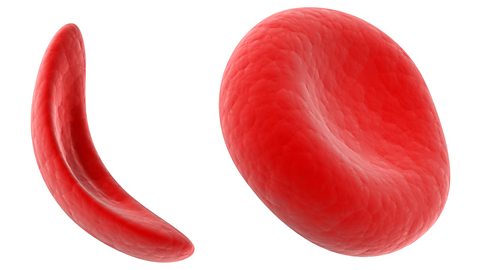
Genetic conditions
Genetic conditions are passed from parents to their children. Learn about conditions that are inherited, such as sickle cell disorder and cystic fibrosis.
Darwin v Doudna: Who was the greatest scientist?
Compare the work of two great scientists, Darwin and Doudna.

Should extinct species be brought back to life?
Discussing whether extinct species should ever be brought back to like. Can you think like a scientist?

Humans and the environment
Greenhouse gases and climate change
Learn how greenhouse gases warm Earth up, and how human activity is putting dangerous amounts of these gases in the atmosphere, causing climate change.

Bioaccumulation
Learn how pollution can cause toxins to enter the food chain and build up to dangerous levels.

Working scientifically
Working safely in the lab
How can you work safely in the lab? What are the various steps needed in order to do so? How to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols.

Variables
Find out why variables are important in an experiment, including control variables, independent and dependent variables.

Writing a hypothesis and prediction
A hypothesis is an idea about how something works that can be tested using experiments. A prediction says what will happen if the hypothesis is correct.

Planning an experiment
Developing a method is an important part of planning an investigation and it is important to evaluate the validity of each step leading up to the conclusion.

Maths skills for science
Scientific equations and formulae are used to work things out in science. Using standard units means scientists around the world can work together better.

Drawing scientific apparatus
Use diagrams to show how scientific apparatus is set up and how to draw them in 2D. Common practical techniques that use apparatus include filtration, evaporation and distillation.

Observation and measurement skills
Calculating averages from data is usually more accurate than using one result. Using a table ensures that data is recorded in an organised way.

Types of data
Types of data include continuous, discrete and categoric. Data can be presented in a number of ways, which depends on the type of variable and the uses.

Graphs and charts
Different types of graphs and charts are used to show results. They need to be drawn and labelled correctly. Scientists use patterns in the data to reach a conclusion.

Conclude and evaluate
A conclusion sums up what has been found out during an investigation. It should be clearly structured and explained using scientific knowledge.

Bias in science
Scientific studies can be biased; it's important to recognise when this is the case. Scientists review each other's conclusions from new research.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription