Key points
- Cells are the smallest unit of life and the building blocks for all organisms.
- Each component of a cell has its own function.
- Animal and plant cells differ and they have similarities.
- Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria are four cell components that are found in both animal and plant cells.
Game - onion cells
Play an Atomic Labs activity to look at onion cells under a microscope.
You can also play the full game
Magnification of cells activity
Play this game to see what different cells look like through different microscopes.
What are cells?
All life on Earth is made from cells. Without cells, there can be no life.
Almost all cells are so small that you need a microscopeA scientific instrument used to see tiny objects, such as cells, magnified several hundred times or more. to see them. Some organisms, like bacteriaLiving organisms which can only be seen with a microscope. Some bacteria cause disease, others are useful. are made of only one cell. These are unicellular organismsUnicellular organisms are made from one cell only, like bacteria.. Others, like trees and blue whales, are made from millions or even billions of cells. These are multicellular organisms. These often have different types of cells, each with a different function. These are specialised cellsCells which have a particular adaptation to allow them to complete a specific function..
What makes up an animal cell?
Each component in the animal cell has a particular function. Animal cells often have an irregular shape.
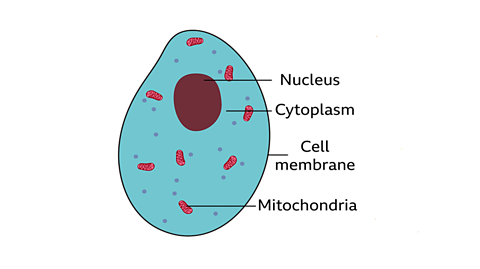
The four key components of most animal cells are:
Nucleus - this contains the genetic material (DNA) of the organism and controls the cellÔÇÖs activities.
Cytoplasm - the liquid that makes up most of the cell in which chemical reactions happen. This is mainly water.
Cell membrane - a flexible outer layer that surrounds the cell and controls which substances can pass into and out from it.
Mitochondria - tiny parts of cells floating in the cytoplasm where energy is released from glucose from food. The mitochondria, found in the cell cytoplasm, are where most respirationA chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria of cells in which glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy. happens.
Activity - Animal cell structure
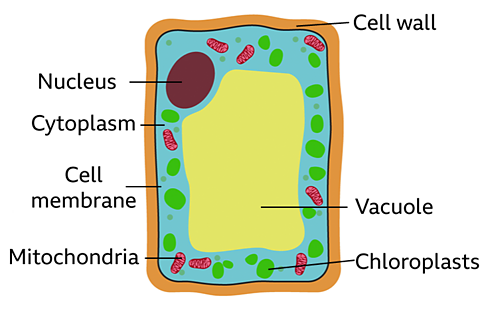
What makes up a plant cell?
Plant cells often have a regular shape. They have the same cell components as animal cells: a nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria.
They also have these extra three as well:
- Cell wall: a tough outer layer of the cell, which contains cellulose to provide strength and support to the plant.
- Vacuole: a space inside the cytoplasm that contains a watery liquid called cell sap. It keeps the cell firm.
- Chloroplasts: structures found in the cells of green parts of plants only (leaves and stems) which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll in which photosynthesisA chemical reaction that occurs in the chloroplasts of plants in which the energy in light is stored in glucose. occurs.
Activity - Plant cell structure
The differences between animal and plant cells
Video
Find out from a greengrocer and a butcher how the structure of a particular cell affects their produce
Tilly: My name's Tilly, I'm a butcher. I cut and sell meat over the counter to the public.
Biology was probably my favourite subject funnily enough. I've always been fascinated with bodies, with animals, with humans, how they work, what they're made up of. Meat is composed of animal cells, the cell membrane, the cytoplasm, and the nucleus. Meat feels squishy, very malleable.
Adam: My name is Adam, and I work for a fruit and vegetable business.
Plant cells have a rigid cell structure. They are made up of a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, and chloroplasts. Plants feel firm because of their cellular walls. This is why fruit and vegetables have a nice crunch and firmness to them.
Tilly: Once you take the bones out of the meat itself, it's very easy to tie it up and change the shape of it.
Adam: Some fruit and vegetables have really strong cells such as root vegetables, carrots, fruits like apples. When they're well-watered, the vacuoles are firm. But when the plant starts to lose water, we start to see the plants going wilted and droopy. We use temperature and humidity to keep the fruit and vegetables fresh.
Tilly: The best thing about being a butcher, I would say for me is talking about how to cook meat, how it's raised, and seeing people choose to buy ethical and sustainable meat.
Adam: Best thing about my job is definitely eating the fruit and vegetables every day.
Can you answer these questions based on the video?
1. What do animal and plant cells feel like?
2. What part of plant cells gives them their crunch?
Animal cells feel squishy or malleable. Plant cells feel firm or rigid.
The cell wall gives plants their crunch.
Test your knowledge
Animal and plant cells quiz
Teaching resources
Looking for more science resources to share with your students? This series of short films explores the science and stories of remarkable people around the world, giving insight into the human body and its capabilities.
┤¾¤¾┤½├¢ Teach has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Living organisms
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 15

- count3 of 15

- count4 of 15
- count5 of 15