Introduction to chromatography
Key points
- Chromatography is a separation technique used to separate mixtures of soluble substances.
- These are often coloured substances such as food colourings, inks, dyes or plant pigments.
- chromatogramThe piece of paper showing results after chromatography has occurred. Analysing the chromatogram allows conclusions to be made about the pigments in the mixture. can be used to match known pigments with those in a mixture.
- On a chromatogram, one spot means that the substance is pure. An impure substance produces two or more spots.
A video about chromatography
A video that shows how chromatography can be used to separate food colourings.
Chromatography is a technique used to separate soluble substances that have been mixed together. It’s normally used to separate coloured mixtures, like food colourings.
We are going to use chromatography to separate these different food colourings into the coloured pigments they are made from.
Start by putting chromatography paper down on a clean flat surface.
Now, use a pencil and ruler to draw a straight line about 1cm from the bottom of the paper.
Dip a wooden toothpick into the first blue food colouring, in this case we are using blue 1.
Put a small spot of colour on to the line.
Now dip a second toothpick into the next food colouring – for us it’s blue 2.
Leave about a 1cm gap between each dot.
We repeat this with yellow 1, yellow 2, and then finally with our green food colouring.
Then use a pencil to label it.
Now attach the paper to a glass rod or pencil using tape.
Put some water into your beaker just deep enough that the very end of the paper goes into the water.
Carefully lower your paper into the water, letting the glass rod balance on the rim of the beaker. Make sure the pencil line is above the surface of the water.
You will notice that the paper absorbs the water and it rises up the chromatography paper past the spots of food colouring. When the water reaches the spots, the pigments will dissolve in the water and move up the paper.
Once the water has stopped rising, you can carefully remove it from the beaker.
You can see that the food colourings have separated out to form a pattern called a chromatogram.
The chromatogram shows us the number of pigments each food colouring contains.
This happens because some pigments are more soluble than others. The more soluble the pigment is, the longer it stays dissolved in the water and the further it travels up the paper.
The yellow and blue food colourings each contain one pigment; they are pure substances.
However, we can see that the green food colouring is a mixture of a blue and yellow pigment. We can tell this because it contains two spots.
What would happen if a coloured sweet was placed in the middle of a circle of filter paper and a few drops of water were added?
The colour from the sweet would move onto the paper and spread out. Usually, the food colour splits into different colours as it moves across the paper.
Separating dissolved solids using chromatography

When a solutionA mixture made when a solute (usually a solid) dissolves into a solvent (a liquid). Sea water is a solution of salt dissolved into water. contains more than one dissolveThe process when a solute is mixed with a solvent and the solute breaks into much smaller particles and spreads out. substance, those substances can be separated using chromatographyA separation technique used to separate mixtures of soluble substances. It is used to separate the pigments in a mixture like ink or food colouring. .
This is especially easy when the dissolved substances are different coloured pigmentA coloured substance. Pigments are mixed together to make inks and food colourings.. An ink or food colouring is usually made from more than one pigment dissolved in water. Chromatography can be used to separate the pigments in ink or food colouring.

Chromatography works because some of the pigments are more solubleA solid is soluble if it can dissolve into a specific solvent. For example, salt and sugar are both soluble in water. in water than others. Pigments with a higher solubilityA measurement of how soluble a solute is in a specific solvent. If the solubility is high, it means that the solute is very soluble in the solvent. move further up the paper.
There are two methods that can be used in chromatography:
- standard chromatography
- radial chromatography
Standard chromatography
The photo shows an example of a chromatogramThe piece of paper showing results after chromatography has occurred. Analysing the chromatogram allows conclusions to be made about the pigments in the mixture. resulting from standard chromatography.
Four samples of ink were used. Looking at the photo from left to right, the first sample on the left is a mixture of pigments (blue and yellow). The other three samples are pure pigments (blue, pink and yellow).

Method
Follow these steps to try out standard chromatography. You will need: a pencil, a ruler, a piece of paper, a coloured mixture such as a food dye.
Draw a horizontal line with a pencil and ruler about 1 cm above the bottom of a piece of chromatography paper.
Place a small spot of the coloured mixtureWhen two or more compounds or elements are present without being chemically bonded together. you are investigating onto the pencil line and allow it to dry.
You might like to add spots of some pure coloured pigments alongside it, so that you can see if they are present in the mixture.
Gently lower the piece of chromatography paper into a beaker which contains a small amount of a suitable solventThe liquid in a solution which dissolves the solute. For example, the solvent in sea water is water., for example, water. The solvent must not cover the pencil line or touch the spots at this stage. You might need to hang the piece of paper from a pencil or a stick resting across the top of the beaker.
Observe as the solvent rises up the piece of paper and reaches the spots on the pencil line.
As the solvent continues to rise, it will dissolve the pigments in the spots and they will start to move. Coloured mixtures will start to separate into spots or ovals which are positioned vertically above where they started.
Look through this slideshow to get a better understanding of standard chromatography.
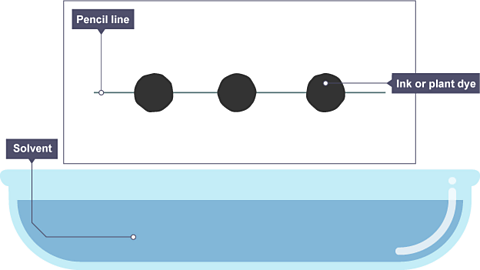
Image caption, A pencil line is drawn, and spots of ink or plant dye are placed on it. There is a container of solvent, such as water or ethanol.
Image caption, The paper is lowered into the solvent. The solvent travels up through the paper, taking some of the coloured substances with it.
Image caption, As the solvent continues to travel up the paper, the different coloured substances spread apart. In this example, the colours separated substances are yellow, red and black.
1 of 3
Radial chromatography
Another technique used to separate pigments in an ink is radial chromatographyA technique used to separate pigments in an ink by adding water onto a spot of ink in the centre of a piece of filter paper. The pigments separate as they move outwards. .
This is done by adding water onto a spot of ink in the centre of a piece of filter paper. The pigments separate as they move outwards from the centre, rather than moving upwards as in standard chromatography.
During standard chromatography, what would happen if the start line on the paper was drawn in pen instead of pencil?
As pens use ink, the pigments in the pen ink would move up the paper with the rising water.
This means it is important to use a pencil (not a pen) when drawing the start line.

Analysing chromatograms
Chromatography is often used to compare an unknown mixture with pure pigments. This allows scientists to see if the mixture contains those pure pigments. Pure pigments which are used in this way are called standard reference pigment A pigment whose identity is known before a chromatography experiment. Standard reference pigments are included in the experiment so that we can see whether they are present in the mixture being investigated..
The piece of paper left at the end of a chromatography experiment is called a chromatogramThe piece of paper showing results after chromatography has occurred. Analysing the chromatogram allows conclusions to be made about the pigments in the mixture. . A chromatogram shows the soluble pigments that were present in the mixture.
Following the process of chromatography, a pure substance will leave just one spot on the chromatogram. The photo demonstrates that the yellow pigment on the left is a pure pigment.

- a mixture will separate into more than one spot, in a vertical column
- the higher the spot, the more soluble the substance
- by matching the colour and height of the spots, you can identify the pigments which were present in the mixture
Using this information, we can work out that in the image above:
- The fourth substance from the left is a mixture made from a yellow pigment and a blue pigment.
- The blue pigment is more soluble in the solvent because it has travelled higher.
- The fourth substance from the left contains the same yellow pigment as the one tested on the left of the chromatogram, and it also contains the same blue pigment as the one tested on the second position from the left.
Quiz
Test your knowledge by trying to analyse these different chromatograms.
What conclusion can be made about a pigment that stays on the start line and does not rise up?
It is insoluble in the solvent.
If a substance is insoluble (not soluble) in the solvent being used, it will remain stationary on the start line.
Conclude and evaluate
In chemistry, a conclusion is information learned from doing an experiment or investigation.
Conclusions should be written in short sentences and use supporting evidence.
From the chromatogram above, five conclusions can be drawn:
The mixture contained three substances because it separated into three spots in a vertical column.
The mixture contained the same red pigment as the standard reference red pigment because the two red spots were the same height.
What are the other three conclusions that can be made from the chromatogram above?
The other three conclusions are:
The mixture contained the same blue pigment as the standard reference red pigment because the two blue spots were the same height.
The mixture contained the same yellow pigment as the standard reference red pigment because the two yellow spots were the same height.
All of the pigments on the chromatogram were soluble in water, because they all moved up from the start line.
Quiz
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Pure and impure substances
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 7

- count5 of 7

- count6 of 7

- count7 of 7
