Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance
Different types of medicines are available to treat many different diseaseIllness affecting plants and animals.. Some medicines only treat the symptoms, whilst others cure the disease by killing the pathogenMicroorganism that causes disease..
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are substances that slow down or stop the growth of bacteriaSingle-celled microorganisms, some of which are pathogenic in humans, animals and plants. Singular is bacterium.. They are commonly prescribed medicines, examples include penicillin and amoxicillin. These can be taken to cure the disease by killing the pathogen, but are only effective against bacterial diseases, not viral ones.
Penicillin
Penicillin is an antibiotic which was discovered by Sir Alexander Fleming in 1928. He noticed that some bacteria he had left in a Petri dishA clear glass or plastic dish, used to grow living cells from organisms so they can be studied. had been killed by the naturally occurring Penicillium mouldA type of fungus..
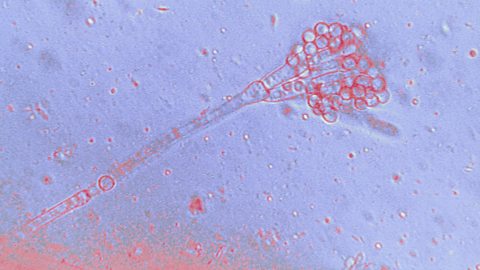
How do antibiotics work?
Antibiotics damage the bacterial cells but do not damage the host cells. They have the ability to cure some bacterial diseases that would have previously killed many people. Since their introduction, they have played a major role in improving health and reducing death rates around the world.
Different bacteria cause different diseases. One particular antibiotic may only work against one or a few types of bacteria. This means that a range of different antibiotics is needed for the treatment of a number of bacterial diseases.
Viral diseases
Viral diseases cannot be cured by antibiotics, because they reproduce inside the host cells.
Antibiotic resistance
Since the discovery of Penicillin in 1928, the use of antibiotics for the treatment of diseases has increased exponentially. As a result, antibioticSubstance that controls the spread of bacteria in the body by killing them or stopping them reproducing. are being overused in many ways in our world today.
Problems with antibiotics
Commonly prescribed antibiotics are becoming less effective due to a number of reasons:
- overuse of antibiotics
- failing to complete the fully prescribed course by a doctor
- use of antibiotics in farming
These can lead to a reduction in the effectiveness of antibiotics, and an increase in the incidence of antibiotic resistanceThe ability of certain bacteria to survive and reproduce in the presence of an antibiotic.. These bacteria are commonly known as superbugs.
One of these superbugs is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is important that there are control measures in place to prevent the spread of this disease. These include:
- hand washing
- thorough cleaning of hospital wards
- use of alcohol gels
- MRSA screening
More guides on this topic
- Classification and biodiversity вҖ“ WJEC
- Cell division and stem cells вҖ“ WJEC
- DNA and inheritance вҖ“ WJEC
- Variation вҖ“ WJEC
- Mutation вҖ“ WJEC
- Evolution вҖ“ WJEC
- The nervous system вҖ“ WJEC
- Homeostasis вҖ“ WJEC
- The role of the kidneys in homeostasis вҖ“ WJEC
- Micro-organisms and their applications вҖ“ WJEC
- Video playlist