Structure of the atom
Atoms are very small. They have a radius of around 1 Г— 1010 metres.
The modern view of the atomThe smallest part of an element that can exist. is of a nucleusThe central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons, and has most of the mass of the atom. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. containing protonSubatomic particle with a positive charge and a relative mass of 1. The relative charge of a proton is +1. and neutronUncharged subatomic particle, with a mass of 1 relative to a proton. The relative charge of a neutron is 0. with smaller electronSubatomic particle, with a negative charge and a negligible mass relative to protons and neutrons. orbiting outside the nucleus.
Each particle has its own charge and its own mass.
| Relative charge | Relative mass | |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 | 1 |
| Neutron | 0 | 1 |
| Electron | -1 | Close to 0 (1, 2,000) |
Mass number and atomic number
Protons and neutrons are the heaviest particles in an atom and as a result they make up most of the massThe amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g). of the atom. The mass of electrons is often not considered to be significant.
The number of protons is what defines the elementA substance made of one type of atom only., i.e. an atom with six protons in its nucleus will always be carbon, and uranium will always have 92 protons.
Key facts: The total number of protons and neutrons is called the nucleon (mass) numberThe number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom.and the number of protons is called the proton (atomic) numberThe number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. .
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is always the same as the number of protons. If the atom becomes ioniseTo ionise is to convert an uncharged atom or molecule into a charged particle by adding or removing electrons. however, the number of electrons will change. An ion is an atom that has lost or gained one or more electron.
Using atomic symbols
Mass number and atomic number are two important pieces of information about an atom.
An atom can be represented using the symbol notation:
\(_{Z}^{A}\textrm{X}\)
Where:
- A is the mass number
- Z is the atomic number
- X is the symbol
For example, chlorine (Cl) can be shown as:
This symbol shows that chlorine has 35 particles in the nucleus (protons and neutrons), 17 of which are protons. It also tells us that chlorine has 18 neutrons (35 - 17) and, as the number of electrons and protons are equal in a neutral atom, chlorine also has 17 electrons.
Extended syllabus content: Relative mass
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know about the relative mass and charge of a nucleus. Click 'show more' for this content:
The relative mass of a nucleus is the number of protons and neutrons it contains. Because the mass of a proton is equivalent to a neutron, the relative mass of an atom is the same as its nucleon (mass) number. Neutrons have no charge. Protons are positively charged. So the relative charge of a nucleus depends only upon the number of protons. The relative charge of a nucleus is the same as its proton (atomic) number.
Atoms and isotopes
An elementA substance made of one type of atom only. proton (atomic) numberThe number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. defines it. An element with 17protonSubatomic particle with a positive charge and a relative mass of 1. The relative charge of a proton is +1.will always be chlorine.
However an element's mass numberThe number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. can vary, which means that it can have different numbers of neutronUncharged subatomic particle, with a mass of 1 relative to a proton. The relative charge of a neutron is 0.. So although chlorine has a mass number of 35 which means it has 18 neutrons, it can also have a mass number of 37, which means it has 20 neutrons. The different types of chlorine are called isotopeAtoms of an element with the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons..
Key fact: isotopes are forms of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
There are three isotopes of hydrogen: hydrogen, deuterium (hydrogen-2) and tritium (hydrogen-3):
Carbon has three isotopes: 126C, 136C and 146C. They all contain six protons but six, seven and eight neutrons respectively.
147N and 146C are not isotopes of each other, because although they have the same mass number, they are not the same element. If the number of protons changes, it is a different element.
Example
How many protons does 146C contain?
The atomic number is 6 so 146C contains six protons.
Question
How many neutrons does 146C contain?
Number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number = 14 - 6 = 8 neutrons.
Ions
Normally, atoms are neutral. They have the same number of protonSubatomic particle with a positive charge and a relative mass of 1. The relative charge of a proton is +1.in the nucleusThe central part of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons, and has most of the mass of the atom. The plural of nucleus is nuclei. as they have electronSubatomic particle, with a negative charge and a negligible mass relative to protons and neutrons.orbiting in the energy levelsSpecific amounts of energy that electrons have when they orbit a nucleus is a particular shell. Electrons that gain energy may move to a higher energy level (a shell further from the nucleus). Electrons that lose energy may move to a lower energy level (a shell closer to the nucleus).around the nucleus.
Atoms can, however, lose or gain electrons due to collisions or other interactions. When they do, they form charged particles called ionElectrically charged particle, formed when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons.:
- if the atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positively-charged ion
- if the atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes a negatively-charged ion
A helium atom has two electrons in an energy level outside the nucleus. The atom is neutral as it has two positive protons and two negative electrons.
A helium atom that has lost or gained an electron is an ion.
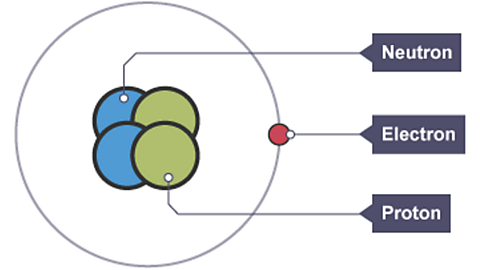
Image caption, The ion has two positive protons but one electron so it is a positive ion. Helium ion, two neutrons, two protons and three electrons.
Image caption, The ion has two positive protons but three electrons so it is a negative ion.
1 of 2
Extended syllabus content: Evidence for the structure of the atom
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know about the evidence for the structure of the atom. Click 'show more' for this content:
In 1909 Ernest Rutherford designed an experiment to test the plum pudding model. In the experiment, positively charged Alpha particlesSubatomic particle comprising two protons and two neutrons (the same as a helium nucleus) were fired at thin gold foil. Most alpha particles went straight through the foil. But a few were scattered in different directions.
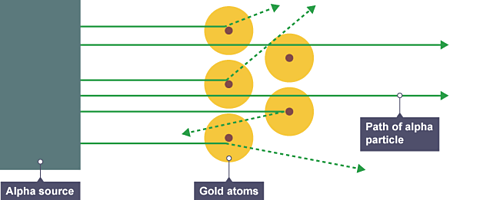
This evidence led Rutherford to suggest a new model for the atom, called the nuclear modelThe scientific idea that an atom has electrons surrounding a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons.. In the nuclear model:
a very small nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space
a nucleus containing most of the mass of the atom
a nucleus with a positive charge.
Extended syllabus content: Nuclear fission
If you are studying the Extended syllabus, you will also need to know about nuclear fission. Click 'show more' for this content:
nuclear fissionThe splitting of a large nucleus to produce two smaller ones. Two or three neutrons are also released in the process. The energy from the neutrons powers a nuclear reactor. is the splitting of a large atomic nucleus into smaller nuclei.
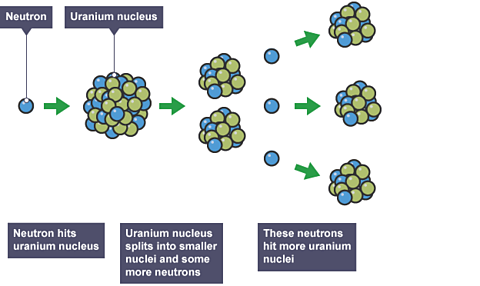
In a nuclear reactorA piece of equipment in which nuclear fission or fusion takes place., a neutronUncharged subatomic particle, with a mass of 1 relative to a proton. The relative charge of a neutron is 0. is absorbed into a nucleus (typically uranium-235). This causes the nucleus to become uranium-236, which is violently unstable.
The entire nucleus splits into two large fragments called 'daughter nucleiThe nuclei (centres of atoms) that are produced by a nuclear reaction. In nuclear fission the parent nucleus splits into two smaller daughter nuclei and releases energy.'. In addition to the 'daughter' products, two or three neutrons also explode out of the fission reaction and these can collide with other uranium nuclei to cause further fission reactions. This is known as a chain reactionA nuclear chain reaction occurs when a neutron splits a nucleus, releasing more neutrons, which in turn go on to split even more nuclei..
The fast-moving neutrons carry most of the energy from the reaction with them (99%) but before the neutrons can collide with fresh uranium nuclei, they need to be slowed down.
This is so that the energy can pass on to other components in the nuclear reactor, which is used to heat water to drive the turbinesRevolving machine with blades that are turned by wind, water or steam. Turbines in a power station turn the generators. that turn the generatorDevice that converts kinetic energy into electrical energy..
Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz on the nuclear model of the atom.
Teaching resources
Are you a physics teacher looking for more resources? Share this short video with your students:
More on Nuclear physics
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 2
