Motion, forces and energy
Physical quantities and measurement techniques
Units of measurement are are used to represent physical quantities like length, weight and other values. Units can be imperial or metric and can be converted by conversion factors.

Motion
The movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values. These are both used to help in the design of faster and more efficient vehicles.聽

Mass and weight
Mass聽is a measure of the quantity of matter in an object at rest relative to the observer.聽Weight聽is a gravitational force on an object that has mass.聽
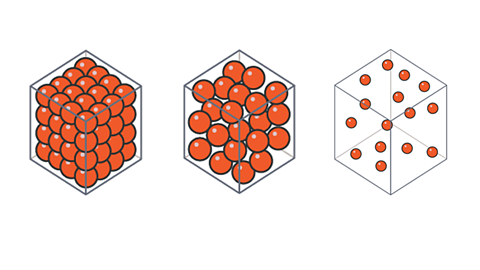
Density
Density describes how closely packed the particles are in a solid, liquid or gas. Matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Atoms can exist on their own or as molecules.
Forces
Forces are responsible for changing the motion of objects. If more than one force is present, the shape of an object can also be changed.聽

Momentum
Momentum can be thought of as a combination of mass and velocity. Momentum helps explain some of the most important interactions in nature.聽

Energy, work and power
Energy is a key principle in physics. The rate at which energy is transferred is called power, the amount of energy that is transferred is called efficiency.聽

Pressure
Every living thing on Earth is in balance with the pressure of the air or water around it. Pressure helps blood to move around the body and allows organisms to breathe.

Forces podcast
Learn all about forces for your IGCSE physics exams, with scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer.

Energy podcast
Learn all about energy for your IGCSE physics exam with this podcast.

- 6 videos

Thermal physics
Kinetic particle model of matter
The three states of matter can be represented by the particle model. This model explains the properties of substances in their different states, as well as changes of state.
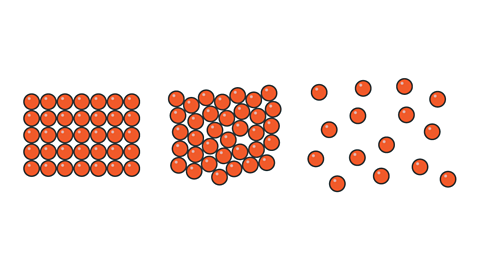
Thermal properties and temperature
Particles are subject to change through either forces or thermal properties. When affected by thermal properties, it will change the bonds that bind them and the state they鈥檙e in.

Transfer of thermal energy
Energy is transmitted by conduction, convection or radiation. The conductivity of materials can be compared by examining the time taken to transmit energy through them.聽

- 5 videos

Waves
General properties of waves
Waves are one way in which energy may be transferred between stores. Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves will transfer energy but not matter.聽

Light
All waves will reflect and refract in the right circumstances. The reflection and refraction of light explains how people see images, colour and even optical illusions.聽
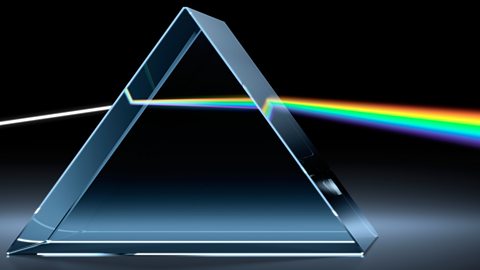
Electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with a wide range of different properties and uses.聽

Sound
Sound is caused by the vibration of particles, not all vibrations can be heard as sound. Common ideas about sound are from the limited range of vibrations that humans can detect.

- 4 videos
Electricity and magnetism
Simple phenomena of magnetism
Magnetism is due to the magnetic fields around magnets. The fields can be investigated by looking at the effects of the forces they exert on other magnets and magnetic materials.

Electrical quantities
The motion of charged particles causes electrical effects, small shocks, lightning and sparks. Electrical fields cause forces to act on charged particles.聽
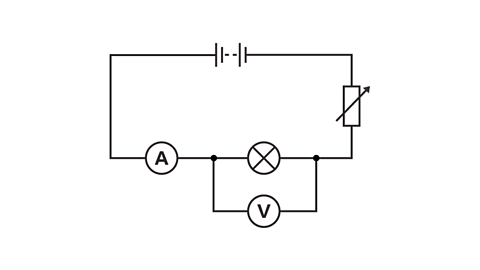
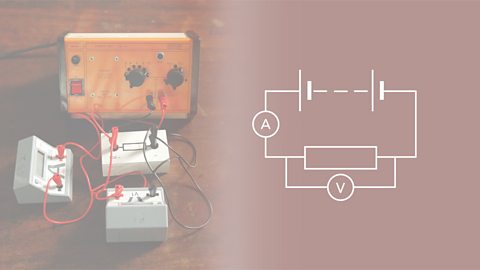
Electric circuits
Electrical currents transfer energy around circuits. There are two types of currents: direct and alternating.聽
Electrical safety
Electrical appliances are designed with features to keep us safe. Electricity can be dangerous due to factors such as there being damp, a wire is damaged or a plug socket overload.

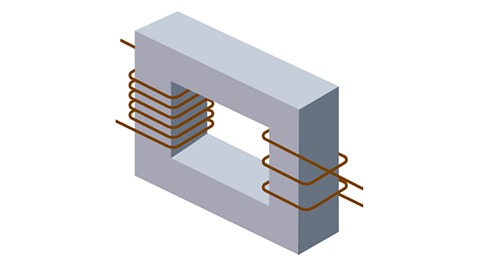
Electromagnetic effects
Electromagnetic induction can create a voltage by movement of a conductor in a magnetic field. The voltage makes current flow, and the effect is used in generation and microphones.
Electricity podcast
Scientists James Stewart and Ellie Hurer guide you through the key facts about electricity for IGCSE physics.

- 3 videos
Nuclear physics
The nuclear model of the atom
Atoms consist of a nucleus with protons and neutrons, encased by electrons. The number of particles in an atom can be calculated from the atom's atomic number and mass number.

Radioactivity
People are exposed to sources of radiation in all aspects of everyday life. Radioactive sources can be very useful but need handling carefully to ensure safety.聽

Space physics
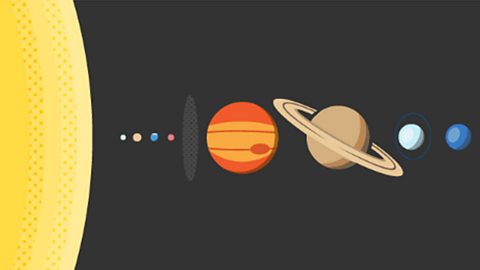
The Earth and the solar system
The solar system is made up of the Sun (our nearest star) and the objects that orbit around it, including planets, asteroids and comets.聽

Stars and the Universe
The Sun is our nearest star. It is a relatively small star when compared to other stars in the universe. Our Solar System contains the Sun and everything that orbits it.
- 2 videos
