Key points
The human body digests carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
These carbohydrates, proteins and fats are digested into nutrients and absorbed into the body.
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions including digestion.
Enzymes
Video - Types of enzyme
VOICEOVER: Enzymes of the digestive system.
Three key types of enzymes in different parts of our digestive system help break down the food to provide the energy our body needs to grow and repair.
They are called carbohydrase enzymes, protease enzymes and lipase enzymes.
Carbohydrates found in starchy and sugary foods are an important source of energy in a healthy diet. When you chew carbohydrate-rich foods, carbohydrase enzymes, such as amylase in your saliva, break down starch into sugar to give us the energy we need. Then protease enzymes in your stomach break down the proteins that will build new cells and repair damaged tissue. Stomach acid helps protease enzymes to destroy harmful microorganisms that may be present in the food.
Fats and oils, or lipids, provide insulation and an energy store for our bodies. Helped by bile from the liver, lipase enzymes break down the lipids into fatty acids and glycerol, so they can be stored.
Cel: Whoa! OK, so our bodies are constantly working without us even knowing about it. That's amazing.
Miss Armit: That, Cel, is the wonder of the human body.
Cel: And it's pretty helpful that each of the three main types of enzymes in the digestive system are named after the food group they help break down.
Miss Armit: Yes, so as we just saw, lipids such as fats and oils are broken down by lipase enzymes.
Cel: Proteins, like meat or pulses, are broken down by protease enzymes.
Miss Armit: And carbohydrates, like bread, are broken down by carbohydrase enzymes. So, are you ready to use your enzymes for the sake of science?
Cel: Well, I'm always looking for new skills for my CV.
Miss Armit: Fab. You'll need that piece of bread just in front of you.
Cel: Oh, you mean my second breakfast?
Miss Armit: Yes. We're going to conduct an experiment to prove what carbohydrase enzymes break carbohydrates down into. Bread contains starch, which is a carbohydrate, so please get munching.
Cel: Oh, you don't have to ask me twice. Here we go.
WITH MOUTH FULL: Lovely.
Cel: Don't swallow it. Mm? Keep chewing. Mm-hm. Yep, keep chewing.
Anything happening?
Cel: Mmā¦ It's getting really mushy.
Miss Armit: Good. Keep going.
Cel: Mm-hm. It's, likeā¦starting to go sweet. You know, like the bread's gone sweet?
Miss Armit: Yes. Carbohydrase enzymes break carbohydrates ā in this case the starch ā into sugar, which is why when you chew for a long time the bread tastes sweet. And as we learned before, the carbohydrase enzyme in saliva is called amylase.
Cel: This is definitely an experiment you can try at home. But, Miss, why does everything we (eat) need to be broken down? I mean, what's the point?
Miss Armit: Good question. We eat food to get the energy and nutrients that our bodies need. If we didn't have enzymes, the molecules of food would be too big to pass into our bloodstream and travel around the body to where they need to be.
Cel: So, carbohydrase and protease and lipase, the three main types of digestive enzymes, are vital to make our bodies work?
Miss Armit: You've got it.
Cel: Awesome. Well, that is someā¦food for thought. Eh?
Can you answer these questions after watching the video?
1. What are the three types of enzymes mentioned in the video?
2. What's in the bread that the presenter eats? What is this broken down into?
Carbohydrase, protease and lipase enzymes.
Starch is in the bread that the presenter eats. This is then broken down into sugar.
Enzymes are protein molecules which act as catalystsChemicals which speed up reactions without being used up. Enzymes are biological catalysts. to speed up reactions. They are not used-up in these reactions. Enzymes can be grouped into two types:
- Those that break larger molecules apart (like digestive enzymes).
- Those that join larger molecules together (like plants making glucose in photosynthesis).
Enzymes have a specific shape. This shape fits into the molecule it will break apart or join together. The part of the enzyme where the molecule fits is called the active siteThe part of an enzyme that fits its substrate or substrates. This changes shape when an enzyme is denatured..
The molecules that enzymes act upon are called substrates. An enzyme is specific for its substrateA molecule or molecules which fit into the active site of an enzyme. like a key is for its lock. This is called the lock and key modelAn enzyme is specific for its substrate or substrates like a key is for its lock..
If enzymes are heated too much or put into a higher or lower pH, their shape can change. The enzyme undertakes a process of denaturation, meaning it will not fit its substrate or substrates. The enzyme cannot speed up the reaction anymore.
Video - Turning starch into glucose
How to turn starch into glucose.
Youāll need some cream crackers, and a glass of water.
Put half a cracker in your mouth and start to chew, making sure you donāt swallow it. At first the taste is quite bland but if you keep chewing for around a minute, it should start to become sweeter. The cream cracker is full of starch.
The saliva in your mouth contains an enzyme called amylase. As you chew the cracker, the amylase triggers the starch to react with water to create a type of sugar called glucose, which tastes sweet. And the amylase reaction carries on making glucose even if you spit out the mush.
If you leave it on a plate for fifteen minutes or so it should taste even sweeter. Thereās only one way to find out.
Can you answer this question based on the video?
What does the amylase enzyme break down into?
A sugar called glucose.
Location of enzymes in the digestive system
This table shows where the types of digestive enzyme are found.
| Enzyme | Location in digestive system |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrase | Mouth, pancreas and small intestine |
| Protease | Stomach, pancreas and small intestine |
| Lipase | Pancreas and small intestine |
Digestion
Chemical digestion occurs when enzymes digest food into nutrients.
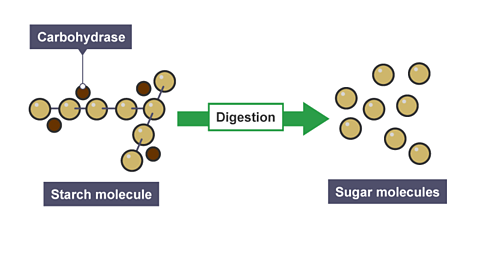
Image caption, Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are digested in the mouth, stomach and small intestine. Carbohydrase enzymes break down starch into sugars.
Image caption, Proteins
Proteins are digested in the stomach and small intestine. Protease enzymes break down proteins into amino acids.
Image caption, Lipids (fats and oils)
Lipase enzymes break down fat into fatty acids and glycerol. Digestion of fat in the small intestine is helped by bile, made in the liver.
1 of 3
Absorption
Digested food molecules are absorbed in the small intestine. This means that they pass through the wall of the small intestine and into the bloodstream. Once there, the digested food molecules are carried around the body to where they are needed.
Only small, soluble substances can pass across the wall of the small intestine. Large insoluble substances cannot pass through.
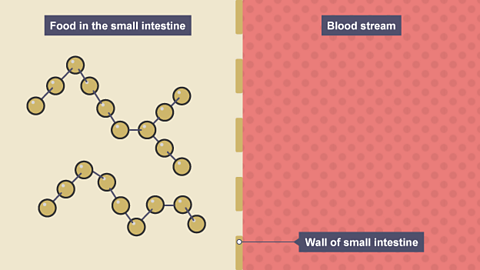
Image caption, Food molecules in the small intestine are too large to pass across its wall and into the bloodstream
Image caption, Carbohydrase enzymes in the small intestine begin to digest the food into smaller molecules
Image caption, The food molecules are now small enough to move by diffusion through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream
1 of 3
Test your knowledge
Quiz - Digestive enzymes and absorption
Test questions
Write an answer to the questions below. Tap 'Show answer' to see the points you could have included.
1. Name the three digestive enzymes and their functions.
2. Describe the lock and key model for the action of enzymes.
Carbohydrase enzymes break down carbohydrates into sugars.
Protease enzymes break down protein into amino acids.
Lipase enzymes break down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol.
Enzymes are protein molecules which have a specific shape.
This fits together with the molecules they are going to break apart of join together.
This area of an enzyme is called an active site.
The molecules that enzymes act upon are called substrates.
An enzyme is specific for its substrate or substrates like a key is for its lock.
Teaching resources
Are you a teacher looking for more resources for your lessons? This video from the Biology with Dr. Chris van Tulleken series explains key scientific concepts and processes related to energy, food chains and food webs.
“óĻó“«Ć½ Teach has thousands of free, curriculum-linked resources to help deliver lessons - all arranged by subject and age group.
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Nutrition, digestion and excretion
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 15

- count4 of 15

- count5 of 15

- count6 of 15
