Key points
- Asthma is a condition that affects the airways carrying air into and out of the lungs.
- Smoking causes lung disease, heart disease and increased risks of several different types of cancer due to its effects on the gas exchange system.
- Exercise increases the demands of the gas exchange system as there is a greater need for oxygen in respiration, and a larger production of carbon dioxide that needs to be removed.
Asthma

Asthma is a very common condition that affects the bronchioles - the small tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs. It is a chronic A condition persisting for a long time or regularly reoccurring. condition with two main components:
- Constriction; the tightening of the muscles surrounding the airways
- Inflammation; the swelling and irritation of the airways.
This may lead to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or shortness of breath.

How does asthma affect the gas exchange system?
When a person with asthma is exposed to a trigger, the airways leading to the lungs become more inflamed or swollen than usual, making it harder to breathe. The airways also get smaller due to a tightening of the muscles surrounding the airways. Finally, the airways can become congested due to a build-up of mucusA sticky substance produced by specialised cells in the body to trap dirt and microbes. which is secreteTo release.by goblet cellsSpecialised cells found in the body that secrete mucus. that line your tracheaThe windpipe..
Symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or shortness of breath can be treated using asthma relievers. Relievers are drugs that relax and open up the airways, making it easier to breathe. Relievers are often administered using a device called an inhaler. This lets you breathe the medicine in through your mouth and directly into your lungs.
Smoking
Smoking is the act of inhaling and exhaling the fumes of burning plant material, most commonly tobacco in a cigarette.
Tobacco smoke contains many harmful substances and carcinogensChemicals which cause cancer. such as:
- Nicotine
- Tar
- Carbon monoxide
How does smoking affect the gas exchange system?
Tobacco smoke
Goblet cells in the lining of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles produce sticky mucus. This traps dirt and pathogensBacteria, fungi and viruses that cause disease.. Cells with tiny hair-like projections called cilliaHair-like projections found on specialised cells. then move the mucus out of the lungs.
Many chemicals in tobacco smoke and tar destroy cilia, which causes mucus to start to build up in the small airways making it harder for the smoker to breathe. This also increases the chance of getting bronchitisA condition which causes inflammation of the airway lining..
Nicotine
Nicotine causes the blood vessels to become narrower, which increases blood pressure. Narrower blood vessels can lead to heart conditions such as coronary heart disease as these blood vessels are more susceptible to become blocked with cholesterol.
The consequence of this blockage is that less red blood cells carrying oxygen will be able to travel to the heart. Therefore, less aerobic respirationA chemical reaction that occurs in all living cells and requires oxygen. can take place in important cells such as the cardiac muscle cells and can lead to a heart attackA serious medical emergency when the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked..
Tar
Tar forms a sticky layer inside the lungs and causes the breakdown of the walls of the alveoliTiny air sacs in the lungs, where gas is exchanged during breathing. causing them to merge together. This reduces the surface area to volume ratio, which means less gas exchange takes place and can lead to emphysemaA condition where less oxygen is carried in the blood making exercise difficult.. Tar also increases the chances of getting lung cancer.
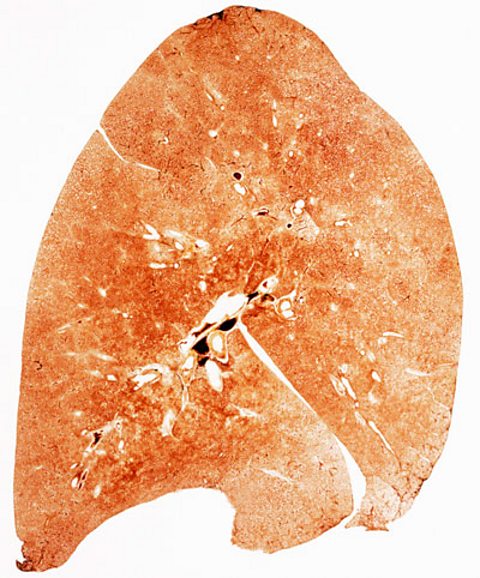
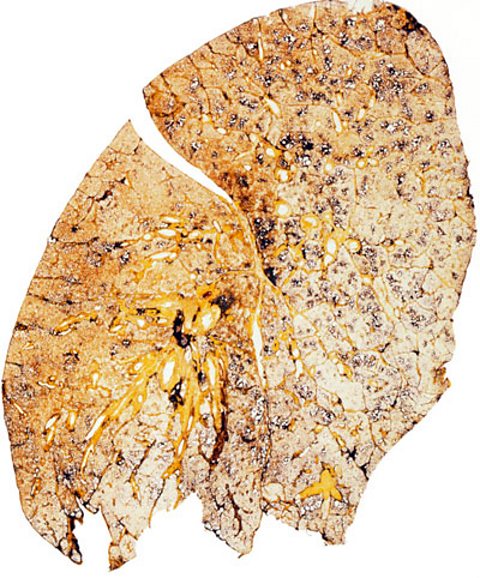
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide binds irreversibly to haemoglobinThe chemical in red blood cells in which oxygen binds to be carried from the lungs to the rest of the body. found in red blood cells, reducing its ability to carry oxygen. This means that the circulatory system has to work harder, increasing the risks of heart disease and strokes.

Did you know?
Cigarette butts are the most littered item on Earth.

Exercise

Exercise causes the frequency and depth of breathing to increase. This can be measured by looking at the following:
Breathing rate (the number of breaths you take per minute)
Tidal volume (the volume of air breathed in and out in one breath)
Increasing the intensity of exercise will mean that the cells in your body are respiring more aerobicRespiration is aerobic when it occurs in the presence of oxygen. so will require more oxygen to be delivered to them, hence the increase in your breathing.

How does exercise affect the gas exchange system?
When a person exercises more, the body grows more new capillariesTiny blood vessels which carry blood into and out of all tissues in the body. a process called capillarisation. Capillarisation takes place at the alveoli in the lungs and in the skeletal muscles. This has the effect of increasing the amount of oxygen that can be transferred to the working muscles as well as increasing the amount of carbon dioxide that can be removed.
Regular exercise also has some additional effects, including an increase in the:
- Strength of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles
- Vital lung capacity; the volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after inhaling fully.
Test your knowledge
Quiz
Test questions
List the chemicals in cigarette smoke and how they can be harmful.
| Nicotine | An addictive drug that narrows blood vessels and can lead to a heart attack. |
| Tar | A black sticky chemical that can cause cancer. |
| Carbon monoxide | A toxic gas that prevents red blood cells from carrying oxygen. |
Play the Atomic Labs game! gamePlay the Atomic Labs game!
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game.

More on Respiration and gas exchange
Find out more by working through a topic
- count8 of 13

- count9 of 13

- count10 of 13