Since 2014, researchers in the (a five-year -funded collaboration between the Universities of , , , and ����ý R&D) have been working on new ways to take immersive audio experiences out of the lab and into the home. All four project partners have labs with large numbers of high-quality loudspeakers—in front of, above, below, and behind the listener (see the picture below for an example from the University of Surrey). In spaces like this, it’s relatively easy to create an immersive sound experience—that is, to give listeners the feeling of being surrounded by or enveloped in sound. But we want to let a wider audience experience great spatial audio in their living rooms without needing to install lots of expensive loudspeakers.
One possible solution is to use the many speakers that people already have at home—in devices like mobile phones, tablets, and laptops—to reproduce parts of the sound scene. We call the idea device orchestration. As part of our research into object-based media, ����ý R&D have been investigating orchestrated media for a number of years, particularly looking at second screen experiences. Research on object-based audio has encouraged us to investigate new audio applications of orchestrated media.
In January 2016, we held a hack week and started prototyping ideas with a showing how we might utilise consumer devices to enhance audio experiences. Since then, we’ve run more formal and studies into whether or not people like this approach to sound reproduction, and how it compares to traditional methods like surround sound. Results have been primarily positive, suggesting that there are benefits over normal stereo reproduction to using orchestrated devices, and that we can achieve a similar quality of listening experience to a well set up surround sound system.
Therefore, we wanted to try out the idea of using orchestrated devices for immersive audio reproduction in the real world, as well as starting to tackle some of the challenges of implementing this outside of the lab. To do this, S3A commissioned a drama specifically to take advantage of using extra connected devices to tell a story—The Vostok-K Incident. You can listen to the piece just like a normal audio drama, but the experience gets better as you connect more extra devices, unlocking immersive spatial aspects as well as extra hidden content.
- The framework for delivering The Vostok-K Incident over the web is being demonstrated at (5–7th June 2019). .
Creating The Vostok-K Incident
The S3A project team worked with Manchester-based production company to design and produce The Vostok-K Incident. We started the process by engaging writer Ed Sellek, describing the technology that we wanted to demonstrate so that he could incorporate relevant ideas into the script. Once the script was written, the next step was fairly similar to a standard radio drama production. We recorded a cast of four actors at Low Four Studios in Manchester.

From then on, the process got more complicated. We set up a production environment in the Usability Lab at ����ý R&D (a space mocked up to look like a living room), with a high-quality stereo pair of loudspeakers augmented by eight small off-the-shelf consumer loudspeakers.
To make the best use of a group of connected speakers, we need to be able to flexibly adapt which sounds are sent to each speaker depending on how many there are and where they’re placed. That requires object-based audio. Rather than sending pre-mixed loudspeaker signals to the home, we send audio objects (elements of the sound scene, like individual voices, sound effects, background sounds, and music) alongside metadata that describe how the sounds should ultimately be reproduced.
- The Vostok-K Incident will be demonstrated at the in October 2018
Metadata often include the desired positions and levels of each sound. However, in this case, we had to capture a much more detailed metadata set in order to compensate for the fact that we didn’t know exactly where the speakers would be, how many there would be, and whether they would be available for the whole duration of the piece. For example, each sound was tagged with a low-resolution target position (e.g. “in front” or “to the side”) as well as fallback positions if no loudspeakers were available in those positions. Researchers from Salford University and ����ý R&D worked closely with the content producers, developing the ruleset for flexible reproduction as needs arose.
We used a (not yet publicly available) created by research software engineers at Southampton University, which enabled us to add new metadata fields as requirements arose during the production.
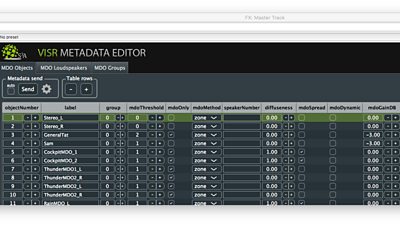
This workflow was challenging, as sound designers are used to making programmes for a known loudspeaker layout—stereo or surround sound, for example. It’s a big departure from the norm to make something that can be enjoyed just as well on a variety of different layouts, particularly when so little is known about the system in advance. Using mobile phones is also tricky because we don’t know exactly how loud they will be or how much delay there will be to each one. We’ve written a bit more about the production process and its challenges in a .
Delivery tools
Once the production was created, we had to work out how to deliver it to the public. This led to three main technical challenges: choosing the right audio (orchestration) to get to the right place (delivery) at the right time (synchronisation). The orchestration rules from the production were implemented as a JavaScript library, so that object routing decisions could be made on the fly. Audio file delivery made use of some extensions to the Web Audio API made by the ����ý R&D audio team, particularly multichannel MPEG DASH streaming and routing. Audio and metadata from the production were converted into a bespoke format; long segments of audio were streamed to the devices, and shorter clips downloaded individually as required.
The synchronisation used a framework developed in the 2-Immerse project, exposing each connected device to a shared timeline and calculating the offset from the device’s own internal time. We can get very good synchronisation in this way, but not perfect alignment. The sound designers were aware of the limitations and could therefore make appropriate choices about the types of sounds to allow into connected speakers. For example, less accuracy is required for dialogue than for rhythmical musical elements.
We also had to think a lot about the steps involved in listening at home, and making the setup as easy as possible. We designed a user interface to go with the story and refined this through a process of user testing and iterative design—starting by working with sketches and mock-ups to collect feedback, and then making refinements that converged towards the finished product. The final interface featured artwork created by the writer, Ed Sellek, alongside design by Naked Productions.


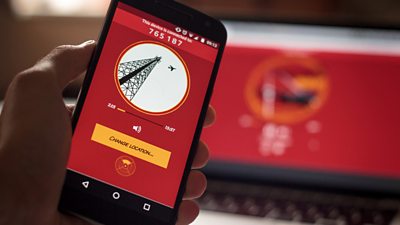
The Vostok-K Incident was launched on ����ý Taster on Thursday 13th September. Members of the S3A project team gave a press conference and then a public lecture at the , and have since given demonstrations at the and the .
What’s next?
As mentioned above, we’ve had promising results from lab tests of orchestrated systems for audio playback. However, this production represents a big step forward in making audio with connected devices available to the public. Creating the piece and developing a system to deliver it were huge learning processes. But there’s also lots we can learn from how the content is received. Are users prepared to connect personal devices to use as speakers? And how can we make this process as easy as possible? What kind of content would this type of immersive, connected spatial audio experience be best suited for? We need to validate that spatial audio with connected devices is a viable proposition and use the feedback to shape further development. Feedback that we’ll get from The Vostok-K Incident on Taster, as well as from formal follow-up experiments run by the S3A team, will be a great way to start answering these questions - so please tell us what you think!
The process we went through to make The Vostok-K Incident has helped us to put tools and workflows in place for creating this type of experience, which should let us make new productions a lot more easily— although there’s still work to be done on making the production process more efficient. Prototyping the connected speaker system using content from a range of genres should help us to uncover the potential benefits. We’ll continue to work out how to get the best sound out of the speakers that are available, whether that’s with clever signal processing, psychoacoustic tricks, or just intelligently picking the best speaker for the job. The trend for extra speakers in the home doesn’t look like slowing down soon, with various smart speakers becoming more and more common. Orchestrated media has exciting potential for making the most of this opportunity.
- -
- ����ý R&D - Vostok K Incident - How we made the Audio Orchestrator - and how you can use it too
- ����ý MakerBox - Audio Orchestrator
- ����ý R&D - Vostok K Incident - Immersive Spatial Sound Using Personal Audio Devices
- ����ý R&D - Vostok-K Incident: Immersive Audio Drama on Personal Devices
- ����ý R&D - Evaluation of an immersive audio experience
- ����ý R&D - Exploring audio device orchestration with audio professionals
- ����ý R&D - Framework for web delivery of immersive audio experiences using device orchestration
- ����ý R&D - The Mermaid's Tears
- ����ý R&D - Talking with Machines
- ����ý R&D - Responsive Radio
-

Immersive and Interactive Content section
IIC section is a group of around 25 researchers, investigating ways of capturing and creating new kinds of audio-visual content, with a particular focus on immersion and interactivity.
